Waves of retrotransposon expansion remodel genome organization and CTCF binding in multiple mammalian lineages
- PMID: 22244452
- PMCID: PMC3368268
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.058
Waves of retrotransposon expansion remodel genome organization and CTCF binding in multiple mammalian lineages
Erratum in
- Cell. 2012 Feb 17;148(4):832
Abstract
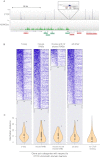
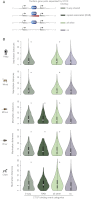
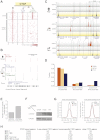
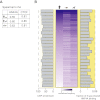
CTCF-binding locations represent regulatory sequences that are highly constrained over the course of evolution. To gain insight into how these DNA elements are conserved and spread through the genome, we defined the full spectrum of CTCF-binding sites, including a 33/34-mer motif, and identified over five thousand highly conserved, robust, and tissue-independent CTCF-binding locations by comparing ChIP-seq data from six mammals. Our data indicate that activation of retroelements has produced species-specific expansions of CTCF binding in rodents, dogs, and opossum, which often functionally serve as chromatin and transcriptional insulators. We discovered fossilized repeat elements flanking deeply conserved CTCF-binding regions, indicating that similar retrotransposon expansions occurred hundreds of millions of years ago. Repeat-driven dispersal of CTCF binding is a fundamental, ancient, and still highly active mechanism of genome evolution in mammalian lineages.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Analysis of the vertebrate insulator protein CTCF-binding sites in the human genome.Cell. 2007 Mar 23;128(6):1231-45. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.048. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17382889 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of in vivo protein-DNA binding sites from ChIP-Seq data.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Sep;36(16):5221-31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn488. Epub 2008 Aug 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18684996 Free PMC article.
-
The human enhancer blocker CTC-binding factor interacts with the transcription factor Kaiso.J Biol Chem. 2005 Dec 30;280(52):43017-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510802200. Epub 2005 Oct 17. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16230345
-
Genome-wide studies of CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) and cohesin provide insight into chromatin structure and regulation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 7;287(37):30906-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R111.324962. Epub 2012 Sep 5. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22952237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CTCF: the protein, the binding partners, the binding sites and their chromatin loops.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 May 6;368(1620):20120369. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2012.0369. Print 2013. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23650640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CTCFBSDB 2.0: a database for CTCF-binding sites and genome organization.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan;41(Database issue):D188-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1165. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23193294 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of enhancer action: the known and the unknown.Genome Biol. 2021 Apr 15;22(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02322-1. Genome Biol. 2021. PMID: 33858480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Young transposable elements rewired gene regulatory networks in human and chimpanzee hippocampal intermediate progenitors.Development. 2022 Oct 1;149(19):dev200413. doi: 10.1242/dev.200413. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Development. 2022. PMID: 36052683 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing throws descriptive 3-D genome folding studies for a loop.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2016 Jul;8(4):286-99. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1338. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27265842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine learning enables pan-cancer identification of mutational hotspots at persistent CTCF binding sites.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Aug 12;52(14):8086-8099. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae530. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38950902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Awad T.A., Bigler J., Ulmer J.E., Hu Y.J., Moore J.M., Lutz M., Neiman P.E., Collins S.J., Renkawitz R., Lobanenkov V.V., Filippova G.N. Negative transcriptional regulation mediated by thyroid hormone response element 144 requires binding of the multivalent factor CTCF to a novel target DNA sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:27092–27098. - PubMed
-
- Baniahmad A., Steiner C., Köhne A.C., Renkawitz R. Modular structure of a chicken lysozyme silencer: involvement of an unusual thyroid hormone receptor binding site. Cell. 1990;61:505–514. - PubMed
-
- Bejerano G., Lowe C.B., Ahituv N., King B., Siepel A., Salama S.R., Rubin E.M., Kent W.J., Haussler D. A distal enhancer and an ultraconserved exon are derived from a novel retroposon. Nature. 2006;441:87–90. - PubMed
-
- Bell A.C., West A.G., Felsenfeld G. The protein CTCF is required for the enhancer blocking activity of vertebrate insulators. Cell. 1999;98:387–396. - PubMed
Supplemental References
-
- Filippova, G.N., Fagerlie, S., Klenova, E.M., Myers, C., Dehner, Y., Goodwin, G., Neiman, P.E., Collins, S.J., and Lobanenkov, V.V. (1996). An exceptionally conserved transcriptional repressor, CTCF, employs different combinations of zinc fingers to bind diverged promoter sequences of avian and mammalian c-myc oncogenes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 2802–2813. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

