Micro- and macrorheology of jellyfish extracellular matrix
- PMID: 22225792
- PMCID: PMC3250689
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.11.4004
Micro- and macrorheology of jellyfish extracellular matrix
Abstract
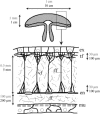
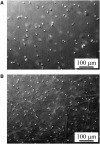
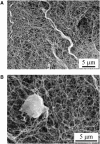
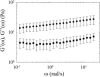
Mechanical properties of the extracellular matrix (ECM) play a key role in tissue organization and morphogenesis. Rheological properties of jellyfish ECM (mesoglea) were measured in vivo at the cellular scale by passive microrheology techniques: microbeads were injected in jellyfish ECM and their Brownian motion was recorded to determine the mechanical properties of the surrounding medium. Microrheology results were compared with macrorheological measurements performed with a shear rheometer on slices of jellyfish mesoglea. We found that the ECM behaved as a viscoelastic gel at the macroscopic scale and as a much softer and heterogeneous viscoelastic structure at the microscopic scale. The fibrous architecture of the mesoglea, as observed by differential interference contrast and scanning electron microscopy, was in accord with these scale-dependent mechanical properties. Furthermore, the evolution of the mechanical properties of the ECM during aging was investigated by measuring microrheological properties at different jellyfish sizes. We measured that the ECM in adult jellyfish was locally stiffer than in juvenile ones. We argue that this stiffening is a consequence of local aggregations of fibers occurring gradually during aging of the jellyfish mesoglea and is enhanced by repetitive muscular contractions of the jellyfish.
Copyright © 2012 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Quantification of local matrix deformations and mechanical properties during capillary morphogenesis in 3D.Integr Biol (Camb). 2012 Apr;4(4):431-9. doi: 10.1039/c2ib00120a. Epub 2012 Jan 26. Integr Biol (Camb). 2012. PMID: 22281872 Free PMC article.
-
Mesogleal cells of the jellyfish Aurelia aurita are involved in the formation of mesogleal fibres.Cell Biol Int. 2005 Nov;29(11):952-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellbi.2005.08.008. Epub 2005 Oct 19. Cell Biol Int. 2005. PMID: 16242363
-
Scyphozoan jellyfish's mesoglea supports attachment, spreading and migration of anthozoans' cells in vitro.Cell Biol Int. 1999;23(4):307-11. doi: 10.1006/cbir.1998.0352. Cell Biol Int. 1999. PMID: 10600239
-
New methods to study the composition and structure of the extracellular matrix in natural and bioengineered tissues.Biomatter. 2012 Jul-Sep;2(3):115-31. doi: 10.4161/biom.20866. Biomatter. 2012. PMID: 23507863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hydrodynamics of Jellyfish Swimming.Ann Rev Mar Sci. 2021 Jan;13:375-396. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-031120-091442. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Ann Rev Mar Sci. 2021. PMID: 32600216 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Morphology of the Cardiac Jelly in the Tubular Heart of Vertebrate Embryos.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2019 Feb 27;6(1):12. doi: 10.3390/jcdd6010012. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2019. PMID: 30818886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-repairing symmetry in jellyfish through mechanically driven reorganization.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jun 30;112(26):E3365-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1502497112. Epub 2015 Jun 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26080418 Free PMC article.
-
Compliant Underwater Manipulator with Integrated Tactile Sensor for Nonlinear Force Feedback Control of an SMA Actuation System.Sens Actuators A Phys. 2020 Nov 1;315:112221. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2020.112221. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Sens Actuators A Phys. 2020. PMID: 34629752 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromechanical wave resonance in jellyfish swimming.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Mar 16;118(11):e2020025118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2020025118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33836589 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome profiling of the dynamic life cycle of the scypohozoan jellyfish Aurelia aurita.BMC Genomics. 2015 Feb 14;16(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1320-z. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25757467 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Discher D.E., Janmey P., Wang Y.L. Tissue cells feel and respond to the stiffness of their substrate. Science. 2005;310:1139–1143. - PubMed
-
- Levental I., Georges P.C., Janmey P.A. Soft biological materials and their impact on cell function. Soft Matter. 2007;3:299–306. - PubMed
-
- Ingber D.E. Mechanical signaling and the cellular response to extracellular matrix in angiogenesis and cardiovascular physiology. Circ. Res. 2002;91:877–887. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

