Deregulation of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in methotrexate chemotherapy-induced damage and recovery of the bone marrow microenvironment
- PMID: 22220905
- PMCID: PMC3385702
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2011.00800.x
Deregulation of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in methotrexate chemotherapy-induced damage and recovery of the bone marrow microenvironment
Abstract
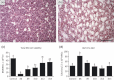
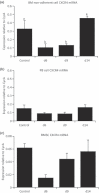
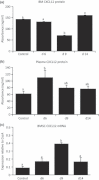
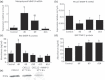
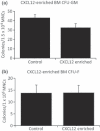
Cancer chemotherapy disrupts the bone marrow (BM) microenvironment affecting steady-state proliferation, differentiation and maintenance of haematopoietic (HSC) and stromal stem and progenitor cells; yet the underlying mechanisms and recovery potential of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression and bone loss remain unclear. While the CXCL12/CXCR4 chemotactic axis has been demonstrated to be critical in maintaining interactions between cells of the two lineages and progenitor cell homing to regions of need upon injury, whether it is involved in chemotherapy-induced BM damage and repair is not clear. Here, a rat model of chemotherapy treatment with the commonly used antimetabolite methotrexate (MTX) (five once-daily injections at 0.75 mg/kg/day) was used to investigate potential roles of CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in damage and recovery of the BM cell pool. Methotrexate treatment reduced marrow cellularity, which was accompanied by altered CXCL12 protein levels (increased in blood plasma but decreased in BM) and reduced CXCR4 mRNA expression in BM HSC cells. Accompanying the lower marrow CXCL12 protein levels (despite its increased mRNA expression in stromal cells) was increased gene and protein levels of metalloproteinase MMP-9 in bone and BM. Furthermore, recombinant MMP-9 was able to degrade CXCL12 in vitro. These findings suggest that MTX chemotherapy transiently alters BM cellularity and composition and that the reduced cellularity may be associated with increased MMP-9 expression and deregulated CXCL12/CXCR4 chemotactic signalling.
© 2012 The Authors. International Journal of Experimental Pathology © 2012 International Journal of Experimental Pathology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 contributes to the mobilization of bone marrow cells in the injured liver.Cell Transplant. 2012;21(2-3):453-64. doi: 10.3727/096368911X605367. Cell Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22793053
-
A critical role of Src family kinase in SDF-1/CXCR4-mediated bone-marrow progenitor cell recruitment to the ischemic heart.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015 Apr;81:49-53. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.01.024. Epub 2015 Feb 3. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25655934 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation of BM SDF-1 by MMP-9: the role in G-CSF-induced hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell mobilization.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008 Nov;42(9):581-8. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2008.222. Epub 2008 Aug 4. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008. PMID: 18679363
-
Damage and recovery of the bone marrow microenvironment induced by cancer chemotherapy - potential regulatory role of chemokine CXCL12/receptor CXCR4 signalling.Curr Mol Med. 2010 Jul;10(5):440-53. doi: 10.2174/156652410791608243. Curr Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20540706 Review.
-
Role of CXCR4 in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia.Theranostics. 2013;3(1):34-9. doi: 10.7150/thno.5150. Epub 2013 Jan 13. Theranostics. 2013. PMID: 23382784 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of methamphetamine on glioblastoma cytotoxicity induced by doxorubicin and methotrexate.Neurotox Res. 2014 Oct;26(3):216-27. doi: 10.1007/s12640-014-9464-1. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Neurotox Res. 2014. PMID: 24652521
-
CXCR4 antagonists suppress small cell lung cancer progression.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):85185-85195. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13238. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27835905 Free PMC article.
-
Low dose methotrexate impaired T cell transmigration through down-regulating CXCR4 expression in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Sep 30;26(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03403-9. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39350214 Free PMC article.
-
MeDiA: Mean Distance Association and Its Applications in Nonlinear Gene Set Analysis.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 27;10(4):e0124620. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124620. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25915206 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling of Cxcl12 receptors, Cxcr4 and Cxcr7 in murine testis development and a spermatogenic depletion model indicates a role for Cxcr7 in controlling Cxcl12 activity.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 2;9(12):e112598. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112598. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25460567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abd-Allah AR, Al-Majed AA, Al-Yahya AA, Fouda SI, Al-Shabana OA. L-Carnitine halts apoptosis and myelosuppression induced by carboplatin in rat bone marrow cell cultures (BMC) Arch. Toxicol. 2005;79:406–413. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed SF, Wallace WH, Kelnar CJ. An anthropometric study of children during intensive chemotherapy for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Horm. Res. 1997;48:178–183. - PubMed
-
- Athanassiadou F, Tragiannidis A, Rousso I, et al. Bone mineral density in survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2006;48:101–104. - PubMed
-
- Balabanian K, Lagane B, Infantino S, et al. The chemokine SDF-1/CXCL12 binds to and signals through the orphan receptor RDC1 in T lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:35760–35766. - PubMed
-
- Banfi A, Podesta M, Fazzuoli L, et al. High-dose chemotherapy shows a dose-dependent toxicity to bone marrow progenitors: a mechanism for post-bone marrow transplantation osteopenia. Cancer. 2001;92:2419–2428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

