Actin retrograde flow and actomyosin II arc contraction drive receptor cluster dynamics at the immunological synapse in Jurkat T cells
- PMID: 22219382
- PMCID: PMC3290643
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-08-0731
Actin retrograde flow and actomyosin II arc contraction drive receptor cluster dynamics at the immunological synapse in Jurkat T cells
Abstract
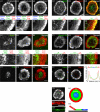
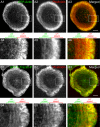
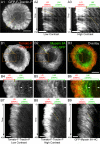
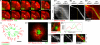
Actin retrograde flow and actomyosin II contraction have both been implicated in the inward movement of T cell receptor (TCR) microclusters and immunological synapse formation, but no study has integrated and quantified their relative contributions. Using Jurkat T cells expressing fluorescent myosin IIA heavy chain and F-tractin-a novel reporter for F-actin-we now provide direct evidence that the distal supramolecular activation cluster (dSMAC) and peripheral supramolecular activation cluster (pSMAC) correspond to lamellipodial (LP) and lamellar (LM) actin networks, respectively, as hypothesized previously. Our images reveal concentric and contracting actomyosin II arcs/rings at the LM/pSMAC. Moreover, the speeds of centripetally moving TCR microclusters correspond very closely to the rates of actin retrograde flow in the LP/dSMAC and actomyosin II arc contraction in the LM/pSMAC. Using cytochalasin D and jasplakinolide to selectively inhibit actin retrograde flow in the LP/dSMAC and blebbistatin to selectively inhibit actomyosin II arc contraction in the LM/pSMAC, we demonstrate that both forces are required for centripetal TCR microcluster transport. Finally, we show that leukocyte function-associated antigen 1 clusters accumulate over time at the inner aspect of the LM/pSMAC and that this accumulation depends on actomyosin II contraction. Thus actin retrograde flow and actomyosin II arc contraction coordinately drive receptor cluster dynamics at the immunological synapse.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Formin-generated actomyosin arcs propel T cell receptor microcluster movement at the immune synapse.J Cell Biol. 2016 Nov 7;215(3):383-399. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201603080. Epub 2016 Oct 31. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27799367 Free PMC article.
-
F-actin polymerization and retrograde flow drive sustained PLCγ1 signaling during T cell activation.J Cell Biol. 2012 Jun 11;197(6):775-87. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201201018. Epub 2012 Jun 4. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22665519 Free PMC article.
-
A B-cell actomyosin arc network couples integrin co-stimulation to mechanical force-dependent immune synapse formation.Elife. 2022 Apr 11;11:e72805. doi: 10.7554/eLife.72805. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35404237 Free PMC article.
-
Origin, Organization, Dynamics, and Function of Actin and Actomyosin Networks at the T Cell Immunological Synapse.Annu Rev Immunol. 2019 Apr 26;37:201-224. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-042718-041341. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Annu Rev Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30576253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Controversy and consensus regarding myosin II function at the immunological synapse.Curr Opin Immunol. 2013 Jun;25(3):300-6. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2013.03.010. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Curr Opin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23623641 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NAADP activates two-pore channels on T cell cytolytic granules to stimulate exocytosis and killing.Curr Biol. 2012 Dec 18;22(24):2331-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.10.035. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Curr Biol. 2012. PMID: 23177477 Free PMC article.
-
Resolution doubling in live, multicellular organisms via multifocal structured illumination microscopy.Nat Methods. 2012 May 13;9(7):749-54. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2025. Nat Methods. 2012. PMID: 22581372 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive rheology and ordering of cell cytoskeleton govern matrix rigidity sensing.Nat Commun. 2015 Jun 25;6:7525. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8525. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26109233 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Biomechanics Controls Protein Mixing and Segregation in Adherent Membranes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 2;22(7):3699. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073699. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33918167 Free PMC article.
-
A LAT-Based Signaling Complex in the Immunological Synapse as Determined with Live Cell Imaging Is Less Stable in T Cells with Regulatory Capability.Cells. 2021 Feb 17;10(2):418. doi: 10.3390/cells10020418. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33671236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aizawa H, Sameshima M, Yahara I. A green fluorescent protein-actin fusion protein dominantly inhibits cytokinesis, cell spreading, and locomotion in Dictyostelium. Cell Struct Funct. 1997;22:335–345. - PubMed
-
- Allingham JS, Smith R, Rayment I. The structural basis of blebbistatin inhibition and specificity for myosin II. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005;12:378–379. - PubMed
-
- Babich A, Burkhardt JK. Lymphocyte signaling converges on microtubules. Immunity. 2011;34:825–827. - PubMed
-
- Billadeau DD, Nolz JC, Gomez TS. Regulation of T-cell activation by the cytoskeleton. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:131–143. - PubMed
-
- Bunnell SC, Barr VA, Fuller CL, Samelson LE. High-resolution multicolor imaging of dynamic signaling complexes in T cells stimulated by planar substrates. Sci STKE. 2003;2003:PL8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

