Expressed antibody repertoires in human cord blood cells: 454 sequencing and IMGT/HighV-QUEST analysis of germline gene usage, junctional diversity, and somatic mutations
- PMID: 22200891
- PMCID: PMC6953429
- DOI: 10.1007/s00251-011-0595-8
Expressed antibody repertoires in human cord blood cells: 454 sequencing and IMGT/HighV-QUEST analysis of germline gene usage, junctional diversity, and somatic mutations
Abstract
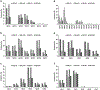
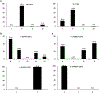
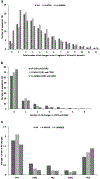
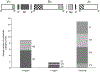
Human cord blood cell-derived IgM antibodies are important for the neonate immune responses and construction of germline-based immunoglobulin libraries. Several previous studies of a relatively small number of sequences found that they exhibit restrictions in the usage of germline genes and in the diversity of the variable heavy chain complementarity determining region 3 compared to adults. To further characterize such restrictions on a larger scale and to compare the early B-cell diversity to adult IgM repertoires, we performed 454 sequencing and IMGT/HighV-QUEST analysis of cord blood IG libraries from two babies and determined germline gene usage, V-D-J rearrangement, VHCDR3 diversity, and somatic mutations to characterize human neonate repertoire. Most of the germline subgroups were identified with frequencies comparable to those present in the adult IgM repertoire except for the IGHV1-2 gene that was preferentially expressed in the cord blood cells. The gene usage diversity contributed to 1,430 unique IGH V-D-J rearrangement patterns while the exonuclease trimming and N region addition at the V-D-J junctions along with gene diversity created a wide range of VHCDR3 with different lengths and sequence variability. We observed a lower degree of somatic mutations in the CDR and framework regions of antibodies from cord blood cells compared to adults. These results provide insights into the characteristics of human cord blood antibody repertoires, which have gene usage diversity and VHCDR3 lengths similar to that of the adult IgM repertoire but differ significantly in some of the gene usages, V-D-J rearrangements, junctional diversity, and somatic mutations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In-Depth Analysis of Human Neonatal and Adult IgM Antibody Repertoires.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 5;9:128. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00128. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29459861 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of human and mouse immunoglobulin variable heavy regions from IMGT/LIGM-DB with IMGT/HighV-QUEST.Theor Biol Med Model. 2014 Jul 3;11:30. doi: 10.1186/1742-4682-11-30. Theor Biol Med Model. 2014. PMID: 24992938 Free PMC article.
-
The restricted DH gene reading frame usage in the expressed human antibody repertoire is selected based upon its amino acid content.J Immunol. 2013 Jun 1;190(11):5567-77. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201929. Epub 2013 Apr 29. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23630353 Free PMC article.
-
Inferred Allelic Variants of Immunoglobulin Receptor Genes: A System for Their Evaluation, Documentation, and Naming.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 18;10:435. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00435. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30936866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism and control of V(D)J recombination at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus.Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:541-70. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115830. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16551259 Review.
Cited by
-
Uncommon structural motifs dominate the antigen binding site in human autoantibodies reactive with basement membrane collagen.Mol Immunol. 2016 Aug;76:123-33. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2016.07.004. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Mol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27450516 Free PMC article.
-
The Antibody Germline/Maturation Hypothesis, Elicitation of Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Against HIV-1 and Cord Blood IgM Repertoires.Front Immunol. 2014 Aug 28;5:398. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00398. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25221552 Free PMC article.
-
The Usage of Human IGHJ Genes Follows a Particular Non-random Selection: The Recombination Signal Sequence May Affect the Usage of Human IGHJ Genes.Front Genet. 2020 Dec 8;11:524413. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.524413. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33363565 Free PMC article.
-
Teleost fish mount complex clonal IgM and IgT responses in spleen upon systemic viral infection.PLoS Pathog. 2013 Jan;9(1):e1003098. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003098. Epub 2013 Jan 10. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23326228 Free PMC article.
-
VDJSeq-Solver: in silico V(D)J recombination detection tool.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 23;10(3):e0118192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118192. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25799103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alamyar E, Giudicelli V, Duroux P, Lefranc MP (2010) IMGT/HighV-QUEST: a high-throughput system and web portal for the analysis of rearranged nucleotide sequences of antigen receptors - High-throughput version of IMGT/V-QUEST 11èmes Journées Ouvertes en Biologie, Informatique et Mathématiques (JOBIM), 7–9 September 2010 Montpellier, France
-
- Alamyar E, Giudicelli V, Duroux P, Lefranc MP (2011) IMGT/HighV-QUEST 2011. 12èmes Journées Ouvertes de Biologie, Informatique et Mathématiques (JOBIM), 28 June–1 July 2011 Paris, France
-
- Bauer K, Zemlin M, Hummel M, Pfeiffer S, Devers S, Zemlin C, Stein H, Versmold HT (2001) The diversity of rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region genes in peripheral blood B cells of preterm infants is restricted by short third complementarity-determining regions but not by limited gene segment usage. Blood 97:1511–1513 - PubMed
-
- Bobrzynski T, Fux M, Vogel M, Stadler MB, Stadler BM, Miescher SM (2005) A high-affinity natural autoantibody from human cord blood defines a physiologically relevant epitope on the Fc epsilon RI alpha. J Immunol 175:6589–6596 - PubMed
-
- Boyd SD, Marshall EL, Merker JD, Maniar JM, Zhang LN, Sahaf B, Jones CD, Simen BB, Hanczaruk B, Nguyen KD, Nadeau KC, Egholm M, Miklos DB, Zehnder JL, Fire AZ (2009) Measurement and Clinical Monitoring of Human Lymphocyte Clonality by Massively Parallel V-D-J Pyrosequencing. Sci Trans Med 1 (12):12ra23 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

