Determinants of small ubiquitin-like modifier 1 (SUMO1) protein specificity, E3 ligase, and SUMO-RanGAP1 binding activities of nucleoporin RanBP2
- PMID: 22194619
- PMCID: PMC3281653
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.321141
Determinants of small ubiquitin-like modifier 1 (SUMO1) protein specificity, E3 ligase, and SUMO-RanGAP1 binding activities of nucleoporin RanBP2
Abstract
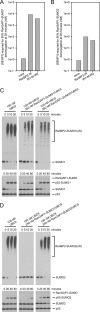
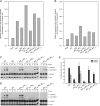
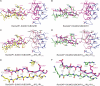
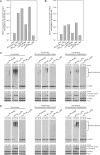
The RanBP2 nucleoporin contains an internal repeat domain (IR1-M-IR2) that catalyzes E3 ligase activity and forms a stable complex with SUMO-modified RanGAP1 and UBC9 at the nuclear pore complex. RanBP2 exhibits specificity for SUMO1 as RanGAP1-SUMO1/UBC9 forms a more stable complex with RanBP2 compared with RanGAP1-SUMO2 that results in greater protection of RanGAP-SUMO1 from proteases. The IR1-M-IR2 SUMO E3 ligase activity also shows a similar preference for SUMO1. We utilized deletions and domain swap constructs in protease protection assays and automodification assays to define RanBP2 domains responsible for RanGAP1-SUMO1 protection and SUMO1-specific E3 ligase activity. Our data suggest that elements in both IR1 and IR2 exhibit specificity for SUMO1. IR1 protects RanGAP1-SUMO1/UBC9 and functions as the primary E3 ligase of RanBP2, whereas IR2 retains the ability to interact with SUMO1 to promote SUMO1-specific E3 ligase activity. To determine the structural basis for SUMO1 specificity, a hybrid IR1 construct and IR1 were used to determine three new structures for complexes containing UBC9 with RanGAP1-SUMO1/2. These structures show more extensive contacts among SUMO, UBC9, and RanBP2 in complexes containing SUMO1 compared with SUMO2 and suggest that differences in SUMO specificity may be achieved through these subtle conformational differences.
Figures

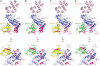
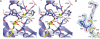
Similar articles
-
The RanBP2/RanGAP1*SUMO1/Ubc9 complex is a multisubunit SUMO E3 ligase.Mol Cell. 2012 May 11;46(3):287-98. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.02.017. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22464730
-
The RanBP2/RanGAP1*SUMO1/Ubc9 SUMO E3 ligase is a disassembly machine for Crm1-dependent nuclear export complexes.Nat Commun. 2016 May 10;7:11482. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11482. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27160050 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into E3 ligase activity revealed by a SUMO-RanGAP1-Ubc9-Nup358 complex.Nature. 2005 Jun 2;435(7042):687-92. doi: 10.1038/nature03588. Nature. 2005. PMID: 15931224 Free PMC article.
-
Protein interactions in the sumoylation cascade: lessons from X-ray structures.FEBS J. 2008 Jun;275(12):3003-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06459.x. Epub 2008 May 17. FEBS J. 2008. PMID: 18492068 Review.
-
Performing in vitro sumoylation reactions using recombinant enzymes.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;497:187-99. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-566-4_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19107418 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the Microscopic Structure of RNF4-SIM-SUMO Complexes from MD Simulations.Biophys J. 2020 Oct 20;119(8):1558-1567. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.09.003. Epub 2020 Sep 11. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 32976759 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of SUMO E3 Ligases in Signaling Pathway of Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 26;23(7):3639. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073639. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SUMO1 Modification of Tau in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Jul;59(7):4419-4435. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02734-5. Epub 2022 May 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35567706 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc controls PML nuclear body formation through regulation of a paralog specific auto-inhibition in SUMO1.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Aug 12;50(14):8331-8348. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac620. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35871297 Free PMC article.
-
The chromatin modification by SUMO-2/3 but not SUMO-1 prevents the epigenetic activation of key immune-related genes during Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus reactivation.BMC Genomics. 2013 Nov 23;14(1):824. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-824. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24267727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson E. S. (2004) Protein modification by SUMO. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 73, 355–382 - PubMed
-
- Geiss-Friedlander R., Melchior F. (2007) Concepts in sumoylation: a decade on. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 947–956 - PubMed
-
- Reindle A., Belichenko I., Bylebyl G. R., Chen X. L., Gandhi N., Johnson E. S. (2006) Multiple domains in Siz SUMO ligases contribute to substrate selectivity. J. Cell Sci. 119, 4749–4757 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

