Cytotoxic CD4 T cells in antiviral immunity
- PMID: 22174559
- PMCID: PMC3228492
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/954602
Cytotoxic CD4 T cells in antiviral immunity
Abstract
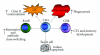
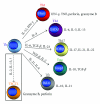
CD4 T cells that acquire cytotoxic phenotype and function have been repeatedly identified in humans, mice, and other species in response to many diverse pathogens. Since CD4 cytotoxic T cells are able to recognize antigenic determinants unique from those recognized by the parallel CD8 cytotoxic T cells, they can potentially contribute additional immune surveillance and direct effector function by lysing infected or malignant cells. Here, we briefly review much of what is known about the generation of cytotoxic CD4 T cells and describe our current understanding of their role in antiviral immunity. Furthering our understanding of the many roles of CD4 T cells during an anti-viral response is important for developing effective vaccine strategies that promote long-lasting protective immunity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The influence of allo-class II MHC-specific Th2 cells on the generation of CD4 and CD8 cytotoxic T cells to associated class I and class II MHC alloantigen.Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 May;100(2):359-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb03677.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7743677 Free PMC article.
-
Class I- and class II-reactive TCRs coexpressed on CD4+ T cells both trigger CD4/CD8-shared and CD4-unique functions.J Immunol. 1997 May 15;158(10):4533-42. J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9144464
-
CD4-deficient mice have reduced levels of memory cytotoxic T lymphocytes after immunization and show diminished resistance to subsequent virus challenge.J Virol. 1996 Feb;70(2):1072-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.70.2.1072-1079.1996. J Virol. 1996. PMID: 8551565 Free PMC article.
-
MHC class II-restricted tumor antigens recognized by CD4+ T cells: new strategies for cancer vaccine design.J Immunother. 2001 May-Jun;24(3):195-204. J Immunother. 2001. PMID: 11394496 Review.
-
Cytotoxic CD4+ T-cells during HIV infection: Targets or weapons?J Clin Virol. 2019 Oct;119:17-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2019.08.004. Epub 2019 Aug 16. J Clin Virol. 2019. PMID: 31445411 Review.
Cited by
-
Host immune response against DENV and ZIKV infections.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Sep 8;12:975222. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.975222. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36159640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clonotypic analysis of protective influenza M2e-specific lung resident Th17 memory cells reveals extensive functional diversity.Mucosal Immunol. 2022 Apr;15(4):717-729. doi: 10.1038/s41385-022-00497-9. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Mucosal Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35260804 Free PMC article.
-
CD4 CTL: living up to the challenge.Semin Immunol. 2013 Nov 15;25(4):273-81. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2013.10.022. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Semin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24246226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD4+ Cytotoxic T Cells Involved in the Development of EBV-Associated Diseases.Pathogens. 2022 Jul 25;11(8):831. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11080831. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35894054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dominant expansion of CD4+, CD8+ T and NK cells expressing Th1/Tc1/Type 1 cytokines in culture-positive lymph node tuberculosis.PLoS One. 2022 May 26;17(5):e0269109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269109. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35617254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wagner H, Starzinski-Powitz A, Jung H, Roellinghoff M. Induction of I region-restricted hapten-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Journal of Immunology. 1977;119(4):1365–1368. - PubMed
-
- Fleischer B. Acquisition of specific cytotoxic activity by human T4+ T lymphocytes in culture. Nature. 1984;308(5957):365–367. - PubMed
-
- Tite JP, Janeway CA., Jr Cloned helper T cells can kill B lymphoma cells in the presence of specific antigen: Ia restriction and cognate vs. noncognate interactions in cytolysis. European Journal of Immunology. 1984;14(10):878–886. - PubMed
-
- Maimone MM, Morrison LA, Braciale VL, Braciale TJ. Features of target cell lysis by class I and class II MHC-restricted cytolytic T lymphocytes. Journal of Immunology. 1986;137(11):3639–3643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

