Hippo signaling in Drosophila: recent advances and insights
- PMID: 22174083
- PMCID: PMC3426292
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.22723
Hippo signaling in Drosophila: recent advances and insights
Abstract
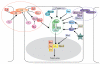
The Hippo signaling pathway emerged from studies of Drosophila tumor suppressor genes, and is now appreciated as a major growth control pathway in vertebrates as well as arthropods. As a recently discovered pathway, key components of the pathway are continually being identified, and new insights into how the pathway is regulated and deployed are arising at a rapid pace. Over the past year and a half, significant advances have been made in our understanding of upstream regulatory inputs into Hippo signaling, key negative regulators of Hippo pathway activity have been identified, and important roles for the pathway in regeneration have been described. This review describes these and other advances, focusing on recent progress in our understanding of Hippo signaling that has come from continued studies in Drosophila.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation-independent repression of Yorkie in Fat-Hippo signaling.Dev Biol. 2009 Nov 1;335(1):188-97. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.08.026. Epub 2009 Sep 3. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19733165 Free PMC article.
-
A role for Hipk in the Hippo pathway.Sci Signal. 2013 May 14;6(275):pe18. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004259. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 23674821 Review.
-
Delineation of a Fat tumor suppressor pathway.Nat Genet. 2006 Oct;38(10):1142-50. doi: 10.1038/ng1887. Epub 2006 Sep 17. Nat Genet. 2006. PMID: 16980976
-
The Hippo size control pathway--ever expanding.Sci Signal. 2013 Jan 22;6(259):pe4. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2003813. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 23354686 Review.
-
YAP-dependent induction of amphiregulin identifies a non-cell-autonomous component of the Hippo pathway.Nat Cell Biol. 2009 Dec;11(12):1444-50. doi: 10.1038/ncb1993. Epub 2009 Nov 22. Nat Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19935651 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Fat1 interacts with Fat4 to regulate neural tube closure, neural progenitor proliferation and apical constriction during mouse brain development.Development. 2015 Aug 15;142(16):2781-91. doi: 10.1242/dev.123539. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Development. 2015. PMID: 26209645 Free PMC article.
-
Vamana Couples Fat Signaling to the Hippo Pathway.Dev Cell. 2016 Oct 24;39(2):254-266. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.09.017. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Dev Cell. 2016. PMID: 27746048 Free PMC article.
-
Mask is required for the activity of the Hippo pathway effector Yki/YAP.Curr Biol. 2013 Feb 4;23(3):229-35. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.12.033. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Curr Biol. 2013. PMID: 23333314 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Hippo signaling promotes Rho1-JNK-dependent growth.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jan 27;112(4):1065-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1415020112. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25583514 Free PMC article.
-
Scribble acts in the Drosophila fat-hippo pathway to regulate warts activity.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e47173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047173. Epub 2012 Nov 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23144804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Badouel C, Gardano L, Amin N, Garg A, Rosenfeld R, Le Bihan T, McNeill H. The FERM-domain protein Expanded regulates Hippo pathway activity via direct interactions with the transcriptional activator Yorkie. Dev Cell. 2009;16:411–420. - PubMed
-
- Bando T, Mito T, Maeda Y, Nakamura T, Ito F, Watanabe T, Ohuchi H, Noji S. Regulation of leg size and shape by the Dachsous/Fat signalling pathway during regeneration. Development. 2009;136:2235–2245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

