Alkane-modified short polyethyleneimine for siRNA delivery
- PMID: 22155553
- PMCID: PMC3814168
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.11.030
Alkane-modified short polyethyleneimine for siRNA delivery
Abstract
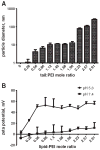
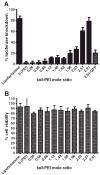
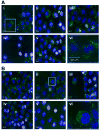
RNA interference (RNAi) is a highly specific gene-silencing mechanism triggered by small interfering RNA (siRNA). Effective intracellular delivery requires the development of potent siRNA carriers. Here, we describe the synthesis and screening of a series of siRNA delivery materials. Short polyethyleneimine (PEI, Mw 600) was selected as a cationic backbone to which lipid tails were conjugated at various levels of saturation. In solution these polymer-lipid hybrids self-assemble to form nanoparticles capable of complexing siRNA. The complexes silence genes specifically and with low cytotoxicity. The efficiency of gene knockdown increased as the number of lipid tails conjugated to the PEI backbone increased. This is explained by reducing the binding affinity between the siRNA strands to the complex, thereby enabling siRNA release after cellular internalization. These results highlight the importance of complexation strength when designing siRNA delivery materials.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Self-assembling polyethylenimine derivatives mediate efficient siRNA delivery in mammalian cells.Chembiochem. 2008 Nov 24;9(17):2787-9. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200800540. Chembiochem. 2008. PMID: 18972467 No abstract available.
-
Impact of lipid substitution on assembly and delivery of siRNA by cationic polymers.Macromol Biosci. 2011 May 12;11(5):662-72. doi: 10.1002/mabi.201000402. Epub 2011 Feb 14. Macromol Biosci. 2011. PMID: 21322108
-
[Small interfering RNA delivery mediated by mPEG-PCL-g-PEI polymer nanoparticles].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2011 Mar;46(3):344-9. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 21626792 Chinese.
-
Polyethylenimines for RNAi-mediated gene targeting in vivo and siRNA delivery to the lung.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011 Apr;77(3):438-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2010.11.007. Epub 2010 Nov 18. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011. PMID: 21093588 Review.
-
Rekindling RNAi Therapy: Materials Design Requirements for In Vivo siRNA Delivery.Adv Mater. 2019 Dec;31(49):e1903637. doi: 10.1002/adma.201903637. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Adv Mater. 2019. PMID: 31566258 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro-in vivo translation of lipid nanoparticles for hepatocellular siRNA delivery.ACS Nano. 2012 Aug 28;6(8):6922-9. doi: 10.1021/nn301922x. Epub 2012 Jul 6. ACS Nano. 2012. PMID: 22770391 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of efficient siRNA carriers in a library of surface-engineered dendrimers.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 28;6:25069. doi: 10.1038/srep25069. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27121799 Free PMC article.
-
Recent In Vivo Evidences of Particle-Based Delivery of Small-Interfering RNA (siRNA) into Solid Tumors.J Pharm Innov. 2014 Jun 1;9(2):158-173. doi: 10.1007/s12247-014-9183-4. J Pharm Innov. 2014. PMID: 25221632 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipid-modified polyethylenimine-based nanopreparations for siRNA-mediated gene silencing: implications for transfection and the role of lipid components.Nanomedicine. 2014 Feb;10(2):411-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2013.07.016. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 23928214 Free PMC article.
-
Degradable terpolymers with alkyl side chains demonstrate enhanced gene delivery potency and nanoparticle stability.Adv Mater. 2013 Mar 13;25(10):1487-93. doi: 10.1002/adma.201204346. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Adv Mater. 2013. PMID: 23293063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Ponnappa BC. siRNA for inflammatory diseases. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009;10:418–424. - PubMed
-
- Garbuzenko OB, Saad M, Betigeri S, Zhang M, Vetcher AA, Soldatenkov VA, Reimer DC, Pozharov VP, Minko T. Intratracheal versus intravenous liposomal delivery of siRNA, antisense oligonucleotides and anticancer drug. Pharm Res. 2009;26:382–394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

