Enhanced desumoylation in murine hearts by overexpressed SENP2 leads to congenital heart defects and cardiac dysfunction
- PMID: 22155005
- PMCID: PMC3294171
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.11.011
Enhanced desumoylation in murine hearts by overexpressed SENP2 leads to congenital heart defects and cardiac dysfunction
Abstract
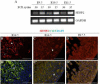
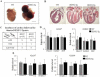
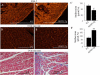
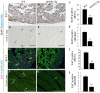
Sumoylation is a posttranslational modification implicated in a variety of cellular activities, and its role in a number of human pathogeneses such as cleft lip/palate has been well documented. However, the importance of the SUMO conjugation pathway in cardiac development and functional disorders is newly emerging. We previously reported that knockout of SUMO-1 in mice led to congenital heart diseases (CHDs). To further investigate the effects of imbalanced SUMO conjugation on heart development and function and its underlying mechanisms, we generated transgenic (Tg) mice with cardiac-specific expression of SENP2, a SUMO-specific protease that deconjugates sumoylated proteins, to evaluate the impact of desumoylation on heart development and function. Overexpression of SENP2 resulted in premature death of mice with CHDs-atrial septal defects (ASDs) and/or ventricular septal defects (VSDs). Immunobiochemistry revealed diminished cardiomyocyte proliferation in SENP2-Tg mouse hearts compared with that in wild type (WT) hearts. Surviving SENP2-Tg mice showed growth retardation, and developed cardiomyopathy with impaired cardiac function with aging. Cardiac-specific overexpression of the SUMO-1 transgene reduced the incidence of cardiac structural phenotypes in the sumoylation defective mice. Moreover, cardiac overexpression of SENP2 in the mice with Nkx2.5 haploinsufficiency promoted embryonic lethality and severity of CHDs, indicating the functional interaction between SENP2 and Nkx2.5 in vivo. Our findings indicate the indispensability of a balanced SUMO pathway for proper cardiac development and function. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled 'Post-translational Modification SI'.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Expression of sumoylation deficient Nkx2.5 mutant in Nkx2.5 haploinsufficient mice leads to congenital heart defects.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20803. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020803. Epub 2011 Jun 3. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21677783 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SENP2-mediated Akt deSUMOylation promotes cardiac regeneration via activating Akt pathway.Clin Sci (Lond). 2021 Mar 26;135(6):811-828. doi: 10.1042/CS20201408. Clin Sci (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33687053
-
Extraembryonic but not embryonic SUMO-specific protease 2 is required for heart development.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 17;6:20999. doi: 10.1038/srep20999. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26883797 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac transcription factor Csx/Nkx2-5: Its role in cardiac development and diseases.Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Aug;107(2):252-68. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.03.005. Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15925411 Review.
-
SUMO1/sentrin/SMT3 specific peptidase 2 modulates target molecules and its corresponding functions.Biochimie. 2018 Sep;152:6-13. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2018.06.007. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Biochimie. 2018. PMID: 29908207 Review.
Cited by
-
SENP1-Mediated HSP90ab1 DeSUMOylation in Cardiomyocytes Prevents Myocardial Fibrosis by Paracrine Signaling.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(34):e2400741. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400741. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38992961 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational Modifications in Heart Failure: Small Changes, Big Impact.Heart Lung Circ. 2016 Apr;25(4):319-24. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2015.11.008. Epub 2015 Dec 4. Heart Lung Circ. 2016. PMID: 26795636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired SIRT1 nucleocytoplasmic shuttling in the senescent heart during ischemic stress.FASEB J. 2013 Nov;27(11):4332-42. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-216473. Epub 2012 Sep 28. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23024374 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation does not affect cardiac troponin I stability but alters indirectly the development of force in response to Ca2.FEBS J. 2022 Oct;289(20):6267-6285. doi: 10.1111/febs.16537. Epub 2022 Jun 8. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 35633070 Free PMC article.
-
Computational study of SENP1 in cancer by novel natural compounds and ZINC database screening.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 12;14:1144632. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1144632. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37502217 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruneau BG, Nemer G, Schmitt JP, Charron F, Robitaille L, Caron S, et al. A murine model of Holt-Oram syndrome defines roles of the T-box transcription factor Tbx5 in cardiogenesis and disease. Cell. 2001;106(6):709–21. - PubMed
-
- Niessen K, Karsan A. Notch signaling in cardiac development. Circ Res. 2008;102(10):1169–81. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka M, Chen Z, Bartunkova S, Yamasaki N, Izumo S. The cardiac homeobox gene Csx/Nkx2.5 lies genetically upstream of multiple genes essential for heart development. Development. 1999;126(6):1269–80. - PubMed
-
- Garg V, Kathiriya IS, Barnes R, Schluterman MK, King IN, Butler CA, et al. GATA4 mutations cause human congenital heart defects and reveal an interaction with TBX5. Nature. 2003;424(6947):443–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

