Interferons in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: regulation and roles
- PMID: 22149411
- PMCID: PMC3234493
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2011.0101
Interferons in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: regulation and roles
Abstract
Several lines of evidence strongly implicate type I interferons (IFN-α and β) and IFN-signaling in the pathogenesis of certain autoimmune inflammatory diseases. Accordingly, genome-wide association studies have identified polymorphisms in the type I IFN-signaling pathways. Other studies also indicate that a feed-forward loop of type I IFN production, which involves sensing of cytoplasmic nucleic acids by sensors, contributes to the development of immunopathology. In addition, a mutually positive regulatory feedback loop between type I IFNs and estrogen receptor-α may contribute to a gender bias, thus resulting in an increased production of type I IFNs and associated immunopathology in women. Increased levels of type I IFNs have numerous immunomodulatory functions for both the innate and adaptive immune responses. Given that the IFN-β also has some anti-inflammatory roles, identifying molecular links among certain genotypes, cytokine profiles, and associated phenotypes in patients with autoimmune inflammatory diseases is likely to improve our understanding of autoimmunity-associated pathogenesis and suboptimal outcomes following standard therapies.
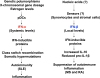
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunomodulatory functions of type I interferons.Nat Rev Immunol. 2012 Jan 6;12(2):125-35. doi: 10.1038/nri3133. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22222875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type1 Interferons Potential Initiating Factors Linking Skin Wounds With Psoriasis Pathogenesis.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 25;10:1440. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01440. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31293591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-4 suppresses dendritic cell response to type I interferons.J Immunol. 2007 Nov 15;179(10):6446-55. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.10.6446. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17982033
-
Rb selectively inhibits innate IFN-β production by enhancing deacetylation of IFN-β promoter through HDAC1 and HDAC8.J Autoimmun. 2016 Sep;73:42-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.05.012. Epub 2016 Jun 4. J Autoimmun. 2016. PMID: 27267461
-
Inborn errors of interferon (IFN)-mediated immunity in humans: insights into the respective roles of IFN-alpha/beta, IFN-gamma, and IFN-lambda in host defense.Immunol Rev. 2008 Dec;226:29-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00698.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 19161414 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of M1 and M2 Macrophages in Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infectivity.J Virol. 2017 Jul 12;91(15):e00578-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00578-17. Print 2017 Aug 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28490589 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-cycle-gated feedback control mediates desensitization to interferon stimulation.Elife. 2020 Sep 18;9:e58825. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58825. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32945770 Free PMC article.
-
The cargo protein MAP17 (PDZK1IP1) regulates the immune microenvironment.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 6;8(58):98580-98597. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21651. eCollection 2017 Nov 17. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29228712 Free PMC article.
-
UMP-CMP kinase 2 gene expression in macrophages is dependent on the IRF3-IFNAR signaling axis.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 27;16(10):e0258989. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258989. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34705862 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term outcomes and risk factors of thyroid dysfunction during pegylated interferon and ribavirin treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection in Taiwan.BMC Endocr Disord. 2019 Apr 5;19(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12902-019-0362-7. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019. PMID: 30953492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aringer M. Smolen JS. Tumour necrosis factor and other proinflammatory cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus: a rationale for therapeutic intervention. Lupus. 2004;13(5):344–347. - PubMed
-
- Baccala R. Gonzalez-Quintial R. Lawson BR. Stern ME. Kono DH. Beutler B. Theofilopoulos AN. Sensors of the innate immune system: their mode of action. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5(8):448–456. - PubMed
-
- Baccala R. Hoebe K. Kono DH. Beutler B. Theofilopoulos AN. TLR-dependent and TLR-independent pathways of type I interferon induction in systemic autoimmunity. Nat Med. 2007;13(5):543–551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical