Pannexins in ischemia-induced neurodegeneration
- PMID: 22147915
- PMCID: PMC3251101
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1018262108
Pannexins in ischemia-induced neurodegeneration
Abstract
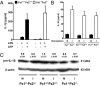
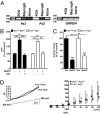
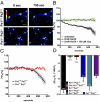
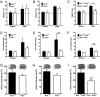
Pannexin 1 (Px1, Panx1) and pannexin 2 (Px2, Panx2) form large-pore nonselective channels in the plasma membrane of cells and were suggested to play a role in the pathophysiology of cerebral ischemia. To directly test a potential contribution of pannexins in ischemia-related mechanisms, we performed experiments in Px1(-/-), Px2(-/-), and Px1(-/-)Px2(-/-) knockout mice. IL-1β release, channel function in astrocytes, and cortical spreading depolarization were not altered in Px1(-/-)Px2(-/-) mice, indicating that, in contrast to previous concepts, these processes occur normally in the absence of pannexin channels. However, ischemia-induced dye release from cortical neurons was lower, indicating that channel function in Px1(-/-)Px2(-/-) neurons was impaired. Furthermore, Px1(-/-)Px2(-/-) mice had a better functional outcome and smaller infarcts than wild-type mice when subjected to ischemic stroke. In conclusion, our data demonstrate that Px1 and Px2 underlie channel function in neurons and contribute to ischemic brain damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional outcome of pannexin-deficient mice after cerebral ischemia.Channels (Austin). 2012 Nov-Dec;6(6):453-6. doi: 10.4161/chan.22315. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Channels (Austin). 2012. PMID: 23111424 Free PMC article.
-
Pannexins, a family of gap junction proteins expressed in brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Nov 11;100(23):13644-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2233464100. Epub 2003 Nov 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14597722 Free PMC article.
-
FGF-1 induces ATP release from spinal astrocytes in culture and opens pannexin and connexin hemichannels.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Dec 28;107(52):22659-64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1013793107. Epub 2010 Dec 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 21148774 Free PMC article.
-
Pannexin channels and their links to human disease.Biochem J. 2014 Aug 1;461(3):371-81. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140447. Biochem J. 2014. PMID: 25008946 Review.
-
Role of connexins and pannexins in ischemic stroke.Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(19):2165-82. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666131228191714. Curr Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24372216 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammasomes link vascular disease with neuroinflammation and brain disorders.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016 Oct;36(10):1668-1685. doi: 10.1177/0271678X16662043. Epub 2016 Aug 2. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016. PMID: 27486046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comparative antibody analysis of pannexin1 expression in four rat brain regions reveals varying subcellular localizations.Front Pharmacol. 2013 Feb 6;4:6. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2013.00006. eCollection 2013. Front Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23390418 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM structure of human heptameric pannexin 2 channel.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 3;14(1):1118. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36861-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36869038 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial cell Pannexin1 modulates severity of ischemic stroke by regulating cerebral inflammation and myogenic tone.JCI Insight. 2018 Mar 22;3(6):e96272. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.96272. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 29563335 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse post-translational modifications of the pannexin family of channel-forming proteins.Channels (Austin). 2014;8(2):124-30. doi: 10.4161/chan.27422. Epub 2014 Jan 13. Channels (Austin). 2014. PMID: 24418849 Free PMC article.
References
-
- MacVicar BA, Thompson RJ. Non-junction functions of pannexin-1 channels. Trends Neurosci. 2010;33:93–102. - PubMed
-
- Lai CP, et al. Tumor-suppressive effects of pannexin 1 in C6 glioma cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67:1545–1554. - PubMed
-
- Bao L, Locovei S, Dahl G. Pannexin membrane channels are mechanosensitive conduits for ATP. FEBS Lett. 2004;572:65–68. - PubMed
-
- Barbe MT, Monyer H, Bruzzone R. Cell-cell communication beyond connexins: The pannexin channels. Physiology (Bethesda) 2006;21:103–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

