CDH3-Related Syndromes: Report on a New Mutation and Overview of the Genotype-Phenotype Correlations
- PMID: 22140374
- PMCID: PMC3214945
- DOI: 10.1159/000327156
CDH3-Related Syndromes: Report on a New Mutation and Overview of the Genotype-Phenotype Correlations
Abstract
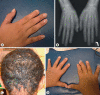
Hypotrichosis with juvenile macular dystrophy (HJMD) and ectodermal dysplasia, ectrodactyly and macular dystrophy (EEM) are both caused by mutations in the CDH3 gene. In this report, we describe a family with EEM syndrome caused by a novel CDH3 gene mutation and review the mutation spectrum and limb abnormalities in both EEM and HJMD. A protein structure model showing the localization of different mutations causing both syndromes is presented. The CDH3 gene was sequenced and investigation of the mutations performed using a protein structure model. The conservation score was calculated by ConSurf. We identified a novel CDH3 gene mutation, p.G277V, which resides in a conserved residue located on a β-strand in the second cadherin domain. Review of the data on previously published mutations showed intra-familial and inter-familial variations in the severity of the limb abnormalities. Syndactyly was the most consistent clinical finding present in all the patients regardless of mutation type. The results of our study point to a phenotypic continuum between HJMD and EEM. It is important for genetic counseling to keep in mind the possible clinical/phenotypic overlap between these 2 syndromes and to be aware of the possible risk of limb abnormalities in future pregnancies in families with HJMD syndrome. CDH3 gene mutation screening is recommended in patients with both these syndromes as part of the work-up in order to offer appropriate genetic counseling.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Distinct CDH3 mutations cause ectodermal dysplasia, ectrodactyly, macular dystrophy (EEM syndrome).J Med Genet. 2005 Apr;42(4):292-8. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2004.027821. J Med Genet. 2005. PMID: 15805154 Free PMC article.
-
P-cadherin is a p63 target gene with a crucial role in the developing human limb bud and hair follicle.Development. 2008 Feb;135(4):743-53. doi: 10.1242/dev.006718. Epub 2008 Jan 16. Development. 2008. PMID: 18199584
-
Splice site mutations in the P-cadherin gene underlie hypotrichosis with juvenile macular dystrophy.Dermatology. 2010;220(3):208-12. doi: 10.1159/000275673. Epub 2010 Mar 5. Dermatology. 2010. PMID: 20203473 Free PMC article.
-
The role of P-cadherin in skin biology and skin pathology: lessons from the hair follicle.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Jun;360(3):761-71. doi: 10.1007/s00441-015-2114-y. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 25707507 Review.
-
Ectodermal dysplasia, ectrodactyly and macular dystrophy (EEM syndrome) in siblings.Am J Med Genet. 2001 Jul 1;101(3):195-7. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1361. Am J Med Genet. 2001. PMID: 11424132 Review.
Cited by
-
A unique case of vision loss in a patient with hypotrichosis and juvenile macular dystrophy and primary ciliary dyskinesia.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2019 Jun 5;15:100486. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2019.100486. eCollection 2019 Sep. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31431935 Free PMC article.
-
The first Japanese family of CDH3-related hypotrichosis with juvenile macular dystrophy.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021 Jun;9(6):e1688. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1688. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021. PMID: 33837674 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Hair Disorders: A Review.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019 Sep;9(3):421-448. doi: 10.1007/s13555-019-0313-2. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019. PMID: 31332722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New CDH3 mutation in the first Spanish case of hypotrichosis with juvenile macular dystrophy, a case report.BMC Med Genet. 2017 Jan 7;18(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12881-016-0364-5. BMC Med Genet. 2017. PMID: 28061825 Free PMC article.
-
Sparse scalp hair and vision loss: think hypotrichosis with juvenile macular dystrophy.BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Oct 23;12(10):e232342. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-232342. BMJ Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31645385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albrectsen B, Svendsen IB. Hypotrichosis, syndactyly, and retinal degeneration in two siblings. Acta Derm Venereol. 1956;36:96–101. - PubMed
-
- Balarin Silva V, Simões AM, Marques-de-Faria AP. EEM syndrome: report of a family and results of a ten-year follow-up. Ophthalmic Genet. 1999;20:95–99. - PubMed
-
- Basit S, Wali A, Aziz A, Muhammad N, Jelani M, Ahmad W. Digenic inheritance of an autosomal recessive hypotrichosis in two consanguineous pedigrees. Clin Genet. 2011;79:273–281. - PubMed
-
- Faraldo MM, Teulière J, Deugnier MA, Birchmeier W, Huelsken J, et al. beta-Catenin regulates P-cadherin expression in mammary basal epithelial cells. FEBS Lett. 2007;581:831–836. - PubMed
-
- He W, Cowin P, Stokes DL. Untangling desmosomal knots with electron tomography. Science. 2003;302:109–113. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

