Proteomic alteration of Marc-145 cells and PAMs after infection by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus
- PMID: 22137209
- PMCID: PMC7112595
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2011.11.005
Proteomic alteration of Marc-145 cells and PAMs after infection by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus
Abstract
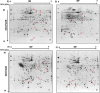
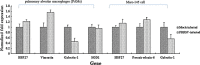
Viral infections usually result in alterations in the host cell proteome, which determine the fate of infected cells and the progress of pathogenesis. To uncover cellular protein responses in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV), infected pulmonary alveolar macrophages (PAMs) and Marc-145 cells were subjected to proteomic analysis involving two-dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE) followed by MALDI-TOF-MS/MS identification. Altered expression of 44 protein spots in infected cells was identified in 2D gels, of which the 29 characterised by MALDI-TOF-MS/MS included 17 up-regulated and 12 down-regulated proteins. Some of these proteins were further confirmed at the mRNA level using real-time RT-PCR. Moreover, Western blot analysis confirmed the up-regulation of HSP27, vimentin and the down-regulation of galectin-1. Our study is the first attempt to analyze the cellular protein profile of PRRSV-infected Marc-145 cells using proteomics to provide valuable information about the effects of PRRSV-induced alterations on Marc-145 cell function. Further study of the affected proteins may facilitate our understanding of the mechanisms of PRRSV infection and pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of differentially expressed proteins in porcine alveolar macrophages infected with virulent/attenuated strains of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 21;9(1):e85767. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085767. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465692 Free PMC article.
-
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection promotes C1QBP secretion to enhance inflammatory responses.Vet Microbiol. 2020 Feb;241:108563. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.108563. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Vet Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31928703
-
Changes in the cellular proteins of pulmonary alveolar macrophage infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus by proteomics analysis.J Proteome Res. 2009 Jun;8(6):3091-7. doi: 10.1021/pr900002f. J Proteome Res. 2009. PMID: 19341299
-
Differential cellular protein expression in continuous porcine alveolar macrophages regulated by the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nucleocapsid protein.Virus Res. 2010 Jul;151(1):88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.04.003. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Virus Res. 2010. PMID: 20394785
-
Two-dimensional liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry coupled with isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification (iTRAQ) labeling approach revealed first proteome profiles of pulmonary alveolar macrophages infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus.J Proteome Res. 2012 May 4;11(5):2890-903. doi: 10.1021/pr201266z. Epub 2012 Apr 17. J Proteome Res. 2012. PMID: 22486680
Cited by
-
Annexin A2 binds to vimentin and contributes to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus multiplication.Vet Res. 2018 Jul 27;49(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13567-018-0571-5. Vet Res. 2018. PMID: 30053894 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome analysis of differential protein expression in porcine alveolar macrophages regulated by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nsp1β protein.Virus Genes. 2018 Jun;54(3):385-396. doi: 10.1007/s11262-018-1547-2. Epub 2018 Mar 5. Virus Genes. 2018. PMID: 29508239
-
Identification of differentially expressed proteins in porcine alveolar macrophages infected with virulent/attenuated strains of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 21;9(1):e85767. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085767. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465692 Free PMC article.
-
Differential innate immune response of endometrial cells to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus type 1 versus type 2.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 26;18(4):e0284658. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284658. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37099541 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of HSP70 reduces porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus replication in vitro.BMC Microbiol. 2014 Mar 13;14:64. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-14-64. BMC Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24625230 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfonso P., Rivera J., Herna’ez B., Alonso C., Escribano J.M. Identification of cellular proteins modified in response to African swine fever virus infection by proteomics. Proteomics. 2004;4:2037–2046. - PubMed
-
- Barrionuevo P., Beigier-Bompadre M., Ilarregui J.M., Toscano M.A., Bianco G.A., Isturiz M.A., Rabinovich G.A. A novel function for galectin-1 at the crossroad of innate and adaptive immunity: galectin-1 regulates monocyte/macrophage physiology through a nonapoptotic ERK-dependent pathway. J. Immunol. 2007;178:436–445. - PubMed
-
- Blackstock W.P., Weir M.P. Proteomics: quantitative and physical mapping of cellular proteins. Trends Biotechnol. 1999;17:121–127. - PubMed
-
- Duan X., Nauwynck H.J., Pensaert M.B. Virus quantification and identification of cellular targets in the lungs and lymphoid tissues of pigs at different time intervals after inoculation with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Vet. Microbiol. 1997;56:9–19. - PubMed
-
- Emmott E., Rodgers M.A., Macdonald A., McCrory S., Ajuh P., Hiscox J.A. Quantitative proteomics using stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture reveals changes in the cytoplasmic, nuclear, and nucleolar proteomes in Vero cells infected with the coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2010;9:1920–1936. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

