μ-Opioid receptors and regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) proteins: from a symposium on new concepts in mu-opioid pharmacology
- PMID: 22129844
- PMCID: PMC3288798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.10.027
μ-Opioid receptors and regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) proteins: from a symposium on new concepts in mu-opioid pharmacology
Abstract
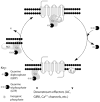
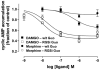
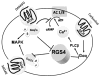
Mu-opioid receptors (MOR) are the therapeutic target for opiate analgesic drugs and also mediate many of the side-effects and addiction liability of these compounds. MOR is a seven-transmembrane domain receptor that couples to intracellular signaling molecules by activating heterotrimeric G proteins. However, the receptor and G protein do not function in isolation but their activities are moderated by several accessory and scaffolding proteins. One important group of accessory proteins is the regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) protein family, a large family of more than thirty members which bind to the activated Gα subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein and serve to accelerate signal termination. This action negatively modulates receptor signaling and subsequent behavior. Several members of this family, in particular RGS4 and RGS9-2 have been demonstrated to influence MOR signaling and morphine-induced behaviors, including reward. Moreover, this interaction is not unidirectional since morphine has been demonstrated to modulate expression levels of RGS proteins, especially RGS4 and RGS9-2, in a tissue and time dependent manner. In this article, I will discuss our work on the regulation of MOR signaling by RGS protein activity in cultured cell systems in the context of other in vitro and behavioral studies. In addition I will consider implications of the bi-directional interaction between MOR receptor activation and RGS protein activity and whether RGS proteins might provide a suitable and novel target for medications to manage addictive behaviors.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mu opioid receptor activation enhances regulator of G protein signaling 4 association with the mu opioid receptor/G protein complex in a GTP-dependent manner.J Neurochem. 2015 Oct;135(1):76-87. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13222. Epub 2015 Jul 16. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26119705 Free PMC article.
-
Differential modulation of mu-opioid receptor signaling to adenylyl cyclase by regulators of G protein signaling proteins 4 or 8 and 7 in permeabilised C6 cells is Galpha subtype dependent.J Neurochem. 2010 Feb;112(4):1026-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06519.x. Epub 2009 Nov 30. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 20002516 Free PMC article.
-
Selective interactions between G protein subunits and RGS4 with the C-terminal domains of the mu- and delta-opioid receptors regulate opioid receptor signaling.Cell Signal. 2006 Jun;18(6):771-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.07.003. Epub 2005 Aug 24. Cell Signal. 2006. PMID: 16120478
-
Effector antagonism by the regulators of G protein signalling (RGS) proteins causes desensitization of mu-opioid receptors in the CNS.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Jun;180(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-2248-9. Epub 2005 Apr 14. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15830230 Review.
-
Regulator of G-Protein Signaling (RGS) Protein Modulation of Opioid Receptor Signaling as a Potential Target for Pain Management.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Jan 24;13:5. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00005. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32038168 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Morphine Drinking Model of Opioid Dependence in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 31;23(7):3874. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073874. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409269 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Regulators of G Protein Signaling Proteins in Bone Physiology and Pathophysiology.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;133:47-75. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.02.002. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 26123302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heat-shock protein 90 (Hsp90) promotes opioid-induced anti-nociception by an ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) mechanism in mouse brain.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jun 23;292(25):10414-10428. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.769489. Epub 2017 Apr 27. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28450396 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of the Mechanisms of Opioid Tolerance: Do We Still Say NO?Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Jul;41(5):927-948. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01065-8. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33704603 Review.
-
βγ G-proteins, but not regulators of G-protein signaling 4, modulate opioid-induced respiratory rate depression.Front Physiol. 2023 Apr 6;14:1043581. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1043581. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37089428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballon DR, Flanary PL, Gladue DP, Konopka JB, Dohlman HG, Thorner J. DEP-domain-mediated regulation of GPCR signaling responses. Cell. 2006;126:1079–1093. - PubMed
-
- Blazer LL, Neubig RR. Small molecule protein-protein interaction inhibitors as CNS therapeutic agents: current progress and future hurdles. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009;34:126–141. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein LS, Ramineni S, Hague C, Cladman W, Chidiac P, Levey AI, Hepler JR. RGS2 binds directly and selectively to the M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor third intracellular loop to modulate Gq/11alpha signaling. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:21248–21256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

