Adenovirus E4-ORF3-dependent relocalization of TIF1α and TIF1γ relies on access to the Coiled-Coil motif
- PMID: 22123502
- PMCID: PMC3249475
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.10.033
Adenovirus E4-ORF3-dependent relocalization of TIF1α and TIF1γ relies on access to the Coiled-Coil motif
Abstract
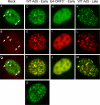
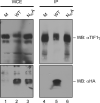
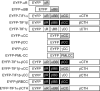
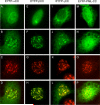
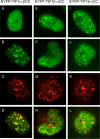
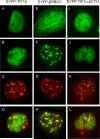
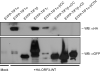
The adenovirus E4-ORF3 protein promotes viral replication by relocalizing cellular proteins into nuclear track structures, interfering with potential anti-viral activities. E4-ORF3 targets transcriptional intermediary factor 1 alpha (TIF1α), but not homologous TIF1β. Here, we introduce TIF1γ as a novel E4-ORF3-interacting partner. E4-ORF3 relocalizes endogenous TIF1γ in virus-infected cells in vivo and binds to TIF1γ in vitro. We used the homologous nature, yet differing binding capabilities, of these proteins to study how E4-ORF3 targets proteins for track localization. We mapped the ability of E4-ORF3 to interact with specific TIF1 subdomains, demonstrating that E4-ORF3 interacts with the Coiled-Coil domains of TIF1α, TIF1β, and TIF1γ, and that the C-terminal half of TIF1β interferes with this interaction. The results of E4-ORF3-directed TIF1 protein relocalization assays performed in vivo were verified using coimmunoprecipitation assays in vitro. These results suggest that E4-ORF3 targets proteins for relocalization through a loosely homologous sequence dependent on accessibility.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TIF1gamma, a novel member of the transcriptional intermediary factor 1 family.Oncogene. 1999 Feb 4;18(5):1209-17. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202655. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10022127
-
Relocalization of the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 complex by the adenovirus E4 ORF3 protein is required for viral replication.J Virol. 2005 May;79(10):6207-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.10.6207-6215.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15858005 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical and functional analyses suggest that adenovirus E4-ORF3 protein requires higher-order multimerization to function against promyelocytic leukemia protein nuclear bodies.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 29;287(27):22573-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.344234. Epub 2012 May 9. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22573317 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus E4orf3 targets transcriptional intermediary factor 1γ for proteasome-dependent degradation during infection.J Virol. 2012 Mar;86(6):3167-79. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06583-11. Epub 2011 Dec 28. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22205733 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional intermediary factor 1 (TIF1) and anti-TIF1γ antibody-positive dermatomyositis.Immunol Med. 2021 Mar;44(1):23-29. doi: 10.1080/25785826.2020.1791402. Epub 2020 Jul 10. Immunol Med. 2021. PMID: 32649853 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of indigo naturalis on colonic mucosal injuries and inflammation in rats with dextran sodium sulphate-induced ulcerative colitis.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Aug;14(2):1327-1336. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4701. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28781623 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus Early Proteins and Host Sumoylation.mBio. 2016 Sep 20;7(5):e01154-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01154-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27651358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Adenovirus E4-ORF3 Oligomerization and Protein Localization on Cellular Gene Expression.Viruses. 2015 May 13;7(5):2428-49. doi: 10.3390/v7052428. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 25984715 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of ubiquitin-like posttranslational modifications induced by the adenovirus E4-ORF3 protein.J Virol. 2015 Feb;89(3):1744-55. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02892-14. Epub 2014 Nov 19. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25410875 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Sirt1 in a rat model of high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Comparison of Gegen Qinlian decoction and resveratrol.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Nov;14(5):4279-4287. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5076. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 29104641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berk AJ. Recent lessons in gene expression, cell cycle control, and cell biology from adenovirus. Oncogene. 2005;24(52):7673–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

