Role of TRPM8 in dorsal root ganglion in nerve injury-induced chronic pain
- PMID: 22111979
- PMCID: PMC3235975
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-12-120
Role of TRPM8 in dorsal root ganglion in nerve injury-induced chronic pain
Abstract
Background: Chronic neuropathic pain is an intractable pain with few effective treatments. Moderate cold stimulation can relieve pain, and this may be a novel train of thought for exploring new methods of analgesia. Transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8) ion channel has been proposed to be an important molecular sensor for cold. Here we investigate the role of TRPM8 in the mechanism of chronic neuropathic pain using a rat model of chronic constriction injury (CCI) to the sciatic nerve.
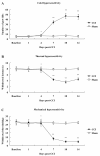
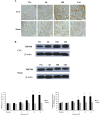
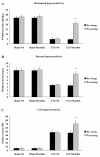
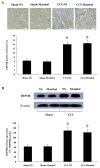
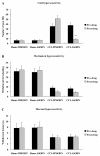
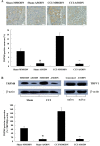
Results: Mechanical allodynia, cold and thermal hyperalgesia of CCI rats began on the 4th day following surgery and maintained at the peak during the period from the 10th to 14th day after operation. The level of TRPM8 protein in L5 dorsal root ganglion (DRG) ipsilateral to nerve injury was significantly increased on the 4th day after CCI, and reached the peak on the 10th day, and remained elevated on the 14th day following CCI. This time course of the alteration of TRPM8 expression was consistent with that of CCI-induced hyperalgesic response of the operated hind paw. Besides, activation of cold receptor TRPM8 of CCI rats by intrathecal application of menthol resulted in the inhibition of mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia and the enhancement of cold hyperalgesia. In contrast, downregulation of TRPM8 protein in ipsilateral L5 DRG of CCI rats by intrathecal TRPM8 antisense oligonucleotide attenuated cold hyperalgesia, but it had no effect on CCI-induced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia.
Conclusions: TRPM8 may play different roles in mechanical allodynia, cold and thermal hyperalgesia that develop after nerve injury, and it is a very promising research direction for the development of new therapies for chronic neuroapthic pain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Downregulations of TRPM8 expression and membrane trafficking in dorsal root ganglion mediate the attenuation of cold hyperalgesia in CCI rats induced by GFRα3 knockdown.Brain Res Bull. 2017 Oct;135:8-24. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.08.002. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Brain Res Bull. 2017. PMID: 28867384
-
TRPM8 mechanism of cold allodynia after chronic nerve injury.J Neurosci. 2007 Dec 12;27(50):13680-90. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2203-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 18077679 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense knock down of TRPA1, but not TRPM8, alleviates cold hyperalgesia after spinal nerve ligation in rats.Exp Neurol. 2006 Jul;200(1):112-23. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.01.031. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Exp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16546170
-
The distinctive role of menthol in pain and analgesia: Mechanisms, practices, and advances.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Oct 5;15:1006908. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1006908. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36277488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of TRPM3 and TRPM8 for sensory neuron sensitisation.Biol Chem. 2024 Oct 1;405(9-10):583-599. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2024-0045. Print 2024 Oct 28. Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39417661 Review.
Cited by
-
Intrathecal TRPM8 blocking attenuates cold hyperalgesia via PKC and NF-κB signaling in the dorsal root ganglion of rats with neuropathic pain.J Pain Res. 2019 Apr 18;12:1287-1296. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S197168. eCollection 2019. J Pain Res. 2019. PMID: 31114308 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct terminal and cell body mechanisms in the nociceptor mediate hyperalgesic priming.J Neurosci. 2015 Apr 15;35(15):6107-16. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5085-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25878283 Free PMC article.
-
Accounting for the delay in the transition from acute to chronic pain: axonal and nuclear mechanisms.J Neurosci. 2015 Jan 14;35(2):495-507. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5147-13.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25589745 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Nociceptor Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) in Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia and Hyperalgesic Priming.J Neurosci. 2019 Aug 14;39(33):6414-6424. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0966-19.2019. Epub 2019 Jun 17. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31209174 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting nociceptive transient receptor potential channels to treat chronic pain: current state of the field.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;175(12):2185-2203. doi: 10.1111/bph.14044. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28924972 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

