Kinome-wide siRNA screening identifies molecular targets mediating the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to Aurora kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 22100984
- PMCID: PMC3265162
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.11.005
Kinome-wide siRNA screening identifies molecular targets mediating the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to Aurora kinase inhibitors
Abstract
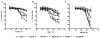
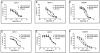
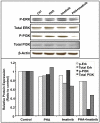
Aurora kinases are a family of mitotic kinases that play important roles in the tumorigenesis of a variety of cancers including pancreatic cancer. A number of Aurora kinase inhibitors (AKIs) are currently being tested in preclinical and clinical settings as anti-cancer therapies. However, the antitumor activity of AKIs in clinical trials has been modest. In order to improve the antitumor activity of AKIs in pancreatic cancer, we utilized a kinome focused RNAi screen to identify genes that, when silenced, would sensitize pancreatic cancer cells to AKI treatment. A total of 17 kinase genes were identified and confirmed as positive hits. One of the hits was the platelet-derived growth factor receptor, alpha polypeptide (PDGFRA), which has been shown to be overexpressed in pancreatic cancer cells and tumor tissues. Imatinib, a PDGFR inhibitor, significantly enhanced the anti-proliferative effect of ZM447439, an Aurora B specific inhibitor, and PHA-739358, a pan-Aurora kinase inhibitor. Further studies showed that imatinib augmented the induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by PHA-739358. These findings indicate that PDGFRA is a potential mediator of AKI sensitivity in pancreatic cancer cells.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Aurora kinase inhibitors as anticancer molecules.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Oct-Dec;1799(10-12):829-39. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.09.004. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20863917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of genes that confer tumor cell resistance to the aurora B kinase inhibitor, AZD1152.Pharmacogenomics J. 2009 Apr;9(2):90-102. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2008.20. Epub 2009 Feb 3. Pharmacogenomics J. 2009. PMID: 19188929
-
Targeting aurora kinases as therapy in multiple myeloma.Blood. 2007 May 1;109(9):3915-21. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-037671. Epub 2007 Jan 9. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17213289 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Growth suppression and mitotic defect induced by JNJ-7706621, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases and aurora kinases.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2012 Jul;12(6):625-39. doi: 10.2174/156800912801784839. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22463590
-
Aurora kinases: new targets for cancer therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Dec 1;12(23):6869-75. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1405. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17145803 Review.
Cited by
-
Target inhibition networks: predicting selective combinations of druggable targets to block cancer survival pathways.PLoS Comput Biol. 2013;9(9):e1003226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003226. Epub 2013 Sep 12. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013. PMID: 24068907 Free PMC article.
-
Aurora kinase a inhibitor MLN8237 suppresses pancreatic cancer growth.Pancreatology. 2022 Jun;22(5):619-625. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2022.03.019. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Pancreatology. 2022. PMID: 35550115 Free PMC article.
-
The pan-Aurora kinase inhibitor, PHA-739358, induces apoptosis and inhibits migration in melanoma cell lines.Melanoma Res. 2013 Apr;23(2):102-13. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0b013e32835df5e4. Melanoma Res. 2013. PMID: 23344158 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking Nerve Growth Factor Signaling Reduces the Neural Invasion Potential of Pancreatic Cancer Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 28;11(10):e0165586. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165586. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27792755 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of posttranslational modifications in pancreatic carcinogenesis and treatments.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021 Sep;40(3):739-759. doi: 10.1007/s10555-021-09980-4. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021. PMID: 34342796 Review.
References
-
- Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, Figer A, Hecht JR, Gallinger S, Au HJ, Murawa P, Walde D, Wolff RA, Campos D, Lim R, Ding K, Clark G, Voskoglou-Nomikos T, Ptasynski M, Parulekar W. Erlotinib Plus Gemcitabine Compared With Gemcitabine Alone in Patients With Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: A Phase III Trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1960–1966. - PubMed
-
- Von Hoff DD, Ramanathan R, Borad M, Laheru D, Smith L, Wood T, Korn R, Desai N, Trieu V, Iglesias J, Zhang H, Soo-shiong P, Shi T, Rajeshkumar NV, Maitra A, Hidalgo M. Gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel Is an active regimen in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: A Phase I/II trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011 Published online on October 3, 2011. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouche O, Guimbaud R, Becouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JL, Gourgou-Bourgade S, de la Fouchardiere C, Bennouna J, Bachet JB, Khemissa-Akouz F, Pere-Verge D, Delbaldo C, Assenat E, Chauffert B, Michel P, Montoto-Grillot C, Ducreux M. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1817–1825. - PubMed
-
- Warner SL, Bearss DJ, Han H, Von Hoff DD. Targeting Aurora-2 Kinase in Cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2003;2:589–595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

