miR-503 represses CUG-binding protein 1 translation by recruiting CUGBP1 mRNA to processing bodies
- PMID: 22072795
- PMCID: PMC3248894
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-05-0456
miR-503 represses CUG-binding protein 1 translation by recruiting CUGBP1 mRNA to processing bodies
Abstract
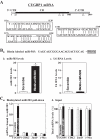
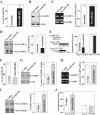
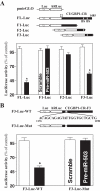
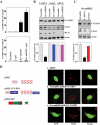
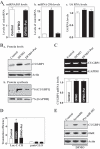
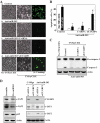
microRNAs (miRNAs) and RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) jointly regulate gene expression at the posttranscriptional level and are involved in many aspects of cellular functions. The RBP CUG-binding protein 1 (CUGBP1) destabilizes and represses the translation of several target mRNAs, but the exact mechanism that regulates CUGBP1 abundance remains elusive. In this paper, we show that miR-503, computationally predicted to associate with three sites of the CUGBP1 mRNA, represses CUGBP1 expression. Overexpression of an miR-503 precursor (pre-miR-503) reduced the de novo synthesis of CUGBP1 protein, whereas inhibiting miR-503 by using an antisense RNA (antagomir) enhanced CUGBP1 biosynthesis and elevated its abundance; neither intervention changed total CUGBP1 mRNA levels. Studies using heterologous reporter constructs revealed a greater repressive effect of miR-503 through the CUGBP1 coding region sites than through the single CUGBP1 3'-untranslated region target site. CUGBP1 mRNA levels in processing bodies (P-bodies) increased in cells transfected with pre-miR-503, while silencing P-body resident proteins Ago2, RCK, or LSm4 decreased miR-503-mediated repression of CUGBP1 expression. Decreasing the levels of cellular polyamines reduced endogenous miR-503 levels and promoted CUGBP1 expression, an effect that was prevented by ectopic miR-503 overexpression. Repression of CUGBP1 by miR-503 in turn altered the expression of CUGBP1 target mRNAs and thus increased the sensitivity of intestinal epithelial cells to apoptosis. These findings identify miR-503 as both a novel regulator of CUGBP1 expression and a modulator of intestinal epithelial homoeostasis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 translation through CUG-binding protein 1 and microRNA-222 by polyamines.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Sep;22(17):3055-69. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-01-0069. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21737690 Free PMC article.
-
Competitive binding of CUGBP1 and HuR to occludin mRNA controls its translation and modulates epithelial barrier function.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Jan;24(2):85-99. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-07-0531. Epub 2012 Nov 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23155001 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative Repression of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Type 2 Receptor Translation by MicroRNA 195 and RNA-Binding Protein CUGBP1.Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Sep 12;37(19):e00225-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00225-17. Print 2017 Oct 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28716948 Free PMC article.
-
Positive and negative modulation of viral and cellular mRNAs by liver-specific microRNA miR-122.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:369-76. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.022. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381319 Review.
-
The coupled and uncoupled mechanisms by which trans-acting factors regulate mRNA stability and translation.J Biochem. 2017 Apr 1;161(4):309-314. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvw086. J Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28039391 Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of RNA-binding protein CELF1 prevents apoptosis and destabilizes pro-apoptotic mRNAs in oral cancer cells.RNA Biol. 2013 Feb;10(2):277-86. doi: 10.4161/rna.23315. Epub 2013 Jan 16. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23324604 Free PMC article.
-
miR-195 competes with HuR to modulate stim1 mRNA stability and regulate cell migration.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Sep;41(16):7905-19. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt565. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23804758 Free PMC article.
-
miR-322/-503 cluster is expressed in the earliest cardiac progenitor cells and drives cardiomyocyte specification.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Aug 23;113(34):9551-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1608256113. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27512039 Free PMC article.
-
CUG-BP1 regulates RyR1 ASI alternative splicing in skeletal muscle atrophy.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 4;5:16083. doi: 10.1038/srep16083. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26531141 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding proteins in eye development and disease: implication of conserved RNA granule components.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016 Jul;7(4):527-57. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1355. Epub 2016 May 1. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016. PMID: 27133484 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baltimore D, Boldin MP, O'Connell RM, Rao DS, Taganov KD. MicroRNAs: new regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:839–845. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya SN, Habermacher R, Martine U, Closs EI, Filipowicz W. Relief of microRNA-mediated translational repression in human cells subjected to stress. Cell. 2006;125:1111–1124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

