A comparison of the anti-tumor effects of a chimeric versus murine anti-CD19 immunotoxins on human B cell lymphoma and Pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines
- PMID: 22069716
- PMCID: PMC3202829
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins3040409
A comparison of the anti-tumor effects of a chimeric versus murine anti-CD19 immunotoxins on human B cell lymphoma and Pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines
Abstract
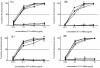
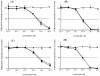
Precursor B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (pre-B ALL) affects five to six thousand adults and almost three thousand children every year. Approximately 25% of the children and 60% of the adults die from their disease, highlighting the need for new therapies that complement rather than overlap chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation. Immunotherapy is a class of therapies where toxicities and mechanisms of action do not overlap with those of chemotherapy. Because CD19 is a B cell- restricted membrane antigen that is expressed on the majority of pre-B tumor cells, a CD19-based immunotherapy is being developed for ALL. In this study, the anti-tumor activities of immunotoxins (ITs) constructed by conjugating a murine monoclonal antibody (MAb), HD37, or its chimeric (c) construct to recombinant ricin toxin A chain (rRTA) were compared both in vitro using human pre-B ALL and Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines and in vivo using a disseminated human pre-B ALL tumor cell xenograft model. The murine and chimeric HD37 IT constructs were equally cytotoxic to pre-B ALL and Burkitt's lymphoma cells in vitro and their use in vivo resulted in equivalent increases in survival of SCID mice with human pre-B ALL tumors when compared with control mice.
Keywords: chimerization; anti-CD19; ricin A chain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chimeric, divalent and tetravalent anti-CD19 monoclonal antibodies with potent in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity against human B-cell lymphoma and pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines.Int J Cancer. 2011 Jul 15;129(2):497-506. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25695. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Int J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 20878959
-
Preclinical studies with the anti-CD19-saporin immunotoxin BU12-SAPORIN for the treatment of human-B-cell tumours.Br J Cancer. 1995 Dec;72(6):1373-9. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.517. Br J Cancer. 1995. PMID: 8519647 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of ricin A chain-containing immunotoxins directed against CD19 and CD22 antigens on normal and malignant human B-cells as potential reagents for in vivo therapy.Cancer Res. 1988 May 1;48(9):2610-7. Cancer Res. 1988. PMID: 2451562 Clinical Trial.
-
CD19: A multifunctional immunological target molecule and its implications for Blineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015 Jul;62(7):1144-8. doi: 10.1002/pbc.25462. Epub 2015 Mar 8. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25755168 Review.
-
Tisagenlecleucel, an approved anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for the treatment of leukemia.Drugs Today (Barc). 2017 Nov;53(11):597-608. doi: 10.1358/dot.2017.53.11.2725754. Drugs Today (Barc). 2017. PMID: 29451276 Review.
Cited by
-
Construction and expression of a human/mouse chimeric CD19 monoclonal antibody: Successful modification of a murine IgM to a chimeric IgG.Exp Ther Med. 2014 Apr;7(4):849-854. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.1511. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Exp Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 24669239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moricke A., Reiter A., Zimmermann M., Gadner H., Stanulla M., Dördelmann M., Löning L., Beier R., Ludwig W.D., Ratei R., et al. Risk-adjusted therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia can decrease treatment burden and improve survival: Treatment results of 2169 unselected pediatric and adolescent patients enrolled in the trial ALL-BFM 95. Blood. 2008;111:4477–4489. - PubMed
-
- Hoelzer D., Gökbuget N., Ottmann O., Pui C.H., Relling M.V., Appelbaum F.R., van Dongen J.J.M., Szczepanski T. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Progr. 2002:162–192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

