Antiviral mode of action of bovine dialyzable leukocyte extract against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection
- PMID: 22044844
- PMCID: PMC3219789
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-4-474
Antiviral mode of action of bovine dialyzable leukocyte extract against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection
Abstract
Background: Bovine dialyzable leukocyte extract (bDLE) is derived from immune leukocytes obtained from bovine spleen. DLE has demonstrated to reduce transcription of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1) and inactivate the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling pathway. Therefore, we decided to clarify the mode of antiviral action of bDLE on the inhibition of HIV-1 infection through a panel of antiviral assays.
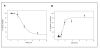
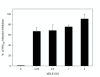
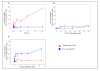
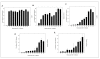
Results: The cytotoxicity, HIV-1 inhibition activity, residual infectivity of bDLE in HIV-1, time of addition experiments, fusion inhibition of bDLE for fusogenic cells and the duration of cell protection even after the removal of bDLE were all assessed in order to discover more about the mode of the antiviral action.HIV-1 infectivity was inhibited by bDLE at doses that were not cytotoxic for HeLa-CD4-LTR-β-gal cells. Pretreatment of HIV-1 with bDLE did not decrease the infectivity of these viral particles. Cell-based fusion assays helped to determine if bDLE could inhibit fusion of Env cells against CD4 cells by membrane fusion and this cell-based fusion was inhibited only when CD4 cells were treated with bDLE. Infection was inhibited in 80% compared with the positive (without EDL) at all viral life cycle stages in the time of addition experiments when bDLE was added at different time points. Finally, a cell-protection assay against HIV-1 infection by bDLE was performed after treating host cells with bDLE for 30 minutes and then removing them from treatment. From 0 to 7 hours after the bDLE was completely removed from the extracellular compartment, HIV-1 was then added to the host cells. The bDLE was found to protect the cells from HIV-1 infection, an effect that was retained for several hours.
Conclusions: bDLE acted as an antiviral compound and prevented host cell infection by HIV-1 at all viral life cycle stages. These cell protection effects lingered for hours after the bDLE was removed. Interestingly, bDLE inhibited fusion of fusogenic cells by acting only on CD4 cells. bDLE had no virucidal effect, but could retain its antiviral effect on target cells after it was removed from the extracellular compartment, protecting the cells from infection for hours.bDLE, which has no reported side effects or toxicity in clinical trials, should therefore be further studied to determine its potential use as a therapeutic agent in HIV-1 infection therapy, in combination with known antiretrovirals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and immunological assessment in breast cancer patients receiving anticancer therapy and bovine dialyzable leukocyte extract as an adjuvant.Exp Ther Med. 2010 May;1(3):425-431. doi: 10.3892/etm_00000066. Epub 2010 May 1. Exp Ther Med. 2010. PMID: 22993557 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro effects of bovine dialyzable leukocyte extract (bDLE) in cancer cells.Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):408-14. doi: 10.1080/14653240600847266. Cytotherapy. 2006. PMID: 16923617
-
Effect of bovine dialyzable leukocyte extract on induction of cell differentiation and death in K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cells.Oncol Lett. 2016 Dec;12(6):4449-4460. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5285. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 28101208 Free PMC article.
-
Peptides derived from the CDR3-homologous domain of the CD4 molecule are specific inhibitors of HIV-1 and SIV infection, virus-induced cell fusion, and postinfection viral transmission in vitro. Implications for the design of small peptide anti-HIV therapeutic agents.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;616:125-48. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb17834.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990. PMID: 2078014 Review.
-
Primate Lentiviruses Modulate NF-κB Activity by Multiple Mechanisms to Fine-Tune Viral and Cellular Gene Expression.Front Microbiol. 2017 Feb 14;8:198. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00198. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28261165 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1)-mediated apoptosis: new therapeutic targets.Viruses. 2014 Aug 19;6(8):3181-227. doi: 10.3390/v6083181. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 25196285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Dialyzable Leukocyte Extract in Autoimmune Prostatitis: Evaluation in Animal Model.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:1832853. doi: 10.1155/2017/1832853. Epub 2017 Mar 12. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28386549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson VA, Brun-Vezinet F, Clotet B, Gunthard HF, Kuritzkes DR, Pillay D. et al.Update of the drug resistance mutations in HIV-1: December 2010. Top HIV Med. 2010;18:156–163. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

