Cellular resistance to HIV-1 infection in target cells coincides with a rapid induction of X-DING-CD4 mRNA: indication of the unique host innate response to virus regulated through function of the X-DING-CD4 gene
- PMID: 22042911
- PMCID: PMC3793846
- DOI: 10.1177/1753425911426893
Cellular resistance to HIV-1 infection in target cells coincides with a rapid induction of X-DING-CD4 mRNA: indication of the unique host innate response to virus regulated through function of the X-DING-CD4 gene
Abstract
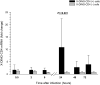
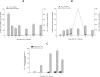
Clinical reports indicate that some infected individuals control HIV-1 replication through undefined mechanisms. Our group reported that a human protein named X-DING-CD4 holds a potent antiviral activity, blocking transcription of HIV-1 LTR through the inhibition of NF-κB/DNA binding. Based on observations that transformed HIV-1 resistant CD4(+) T cells produce higher levels of soluble X-DING-CD4 protein upon their exposure to virus, we hypothesized that resistance to HIV-1 in these cells may be regulated through function of the X-DING-CD4 gene. Real-time PCR evaluations of X-DING-CD4 mRNA expression confirmed our hypothesis; HIV-1 exposure caused rapid up-regulation of X-DING-CD4 mRNA in resistant, but not susceptible, cells; and the burst of X-DING-CD4 mRNA expression correlated with restriction of HIV-1 transcription. Subsequently, we examined the activity of the X-DING-CD4 gene in monocytes and macrophages from (n = 13) HIV-negative donors. The assessment of HIV-1 gag mRNA showed that the majority of cells were permissive to virus replication; however, macrophages from four donors were refractory to HIV-1 infection. In response to virus, these cells up-regulated X-DING-CD4 gene expression by 2- to 1000-fold. These data provide evidence that the X-DING-CD4 gene contributes to early cellular protection from HIV infection in some individuals and this protection depends solely on the unique genetic regulation of the host.
Figures
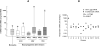
Similar articles
-
Native X-DING-CD4 protein secreted by HIV-1 resistant CD4+ T cells blocks activity of IL-8 promoter in human endothelial cells infected with enteric bacteria.Innate Immun. 2012 Aug;18(4):571-579. doi: 10.1177/1753425911427065. Epub 2011 Oct 26. Innate Immun. 2012. PMID: 22031506 Free PMC article.
-
Human X-DING-CD4 mediates resistance to HIV-1 infection through novel paracrine-like signaling.FEBS J. 2015 Mar;282(5):937-50. doi: 10.1111/febs.13192. Epub 2015 Jan 27. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 25581464 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay between the X-DING-CD4, IFN-α and IL-8 gene activity in quiescent and mitogen- or HIV-1-exposed PBMCs from HIV-1 elite controllers, AIDS progressors and HIV-negative controls.Innate Immun. 2014 Feb;20(2):173-83. doi: 10.1177/1753425913486162. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Innate Immun. 2014. PMID: 23751822 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-mediated restriction of HIV-1 in resting CD4+ T cells and monocytes.Viruses. 2012 Sep;4(9):1390-409. doi: 10.3390/v4091390. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23170164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and cytokine gene expression in myeloid cells by NF-kappa B/Rel transcription factors.Microbiol Rev. 1995 Sep;59(3):481-505. doi: 10.1128/mr.59.3.481-505.1995. Microbiol Rev. 1995. PMID: 7565415 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the Brain Reservoirs: Toward an HIV Cure.Front Immunol. 2016 Sep 30;7:397. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00397. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27746784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Native X-DING-CD4 protein secreted by HIV-1 resistant CD4+ T cells blocks activity of IL-8 promoter in human endothelial cells infected with enteric bacteria.Innate Immun. 2012 Aug;18(4):571-579. doi: 10.1177/1753425911427065. Epub 2011 Oct 26. Innate Immun. 2012. PMID: 22031506 Free PMC article.
-
DING proteins from phylogenetically different species share high degrees of sequence and structure homology and block transcription of HIV-1 LTR promoter.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 6;8(8):e69623. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069623. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936341 Free PMC article.
-
DING Proteins Extend to the Extremophilic World.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 18;22(4):2035. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042035. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33670786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human X-DING-CD4 mediates resistance to HIV-1 infection through novel paracrine-like signaling.FEBS J. 2015 Mar;282(5):937-50. doi: 10.1111/febs.13192. Epub 2015 Jan 27. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 25581464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lamine A, Caumont-Sarcos A, Chaix ML, et al. Replication-competent HIV strains infect HIV controllers despite undetectable viremia (ANRS EP36 study) Aids. 2007;21:1043–5. - PubMed
-
- Migueles SA, Connors M. Long-term nonprogressive disease among untreated HIV-infected individuals: clinical implications of understanding immune control of HIV. Jama. 304:194–201. - PubMed
-
- Shacklett BL. Understanding the “lucky few”: the conundrum of HIV-exposed, seronegative individuals. Current HIV/AIDS reports. 2006;3:26–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

