Looking forward to EphB signaling in synapses
- PMID: 22040917
- PMCID: PMC3646480
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.10.020
Looking forward to EphB signaling in synapses
Abstract
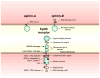
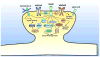
Eph receptors and their ligands ephrins comprise a complex signaling system with diverse functions that span a wide range of tissues and developmental stages. The variety of Eph receptor functions stems from their ability to mediate bidirectional signaling through trans-cellular Eph/ephrin interactions. Initially thought to act by directing repulsion between cells, Ephs have also been demonstrated to induce and maintain cell adhesive responses at excitatory synapses in the central nervous system. EphB receptors are essential to the development and maintenance of dendritic spines, which accommodate the postsynaptic sites of most glutamatergic excitatory synapses in the brain. Functions of EphB receptors are not limited to control of the actin cytoskeleton in dendritic spines, as EphB receptors are also involved in the formation of functional synaptic specializations through the regulation of glutamate receptor trafficking and functions. In addition, EphB receptors have recently been linked to the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease and neuropathic pain, thus becoming promising targets for therapeutic interventions. In this review, we discuss recent findings on EphB receptor functions in synapses, as well as the mechanisms of bidirectional trans-synaptic ephrin-B/EphB receptor signaling that shape dendritic spines and influence post-synaptic differentiation.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bidirectional modulation of synaptic functions by Eph/ephrin signaling.Nat Neurosci. 2009 Jan;12(1):15-20. doi: 10.1038/nn.2231. Epub 2008 Nov 23. Nat Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19029886 Review.
-
Ephrin regulation of synapse formation, function and plasticity.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2012 May;50(1):35-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2012.03.004. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22449939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EphBs and ephrin-Bs: Trans-synaptic organizers of synapse development and function.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018 Sep;91:108-121. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2018.07.002. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30031105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bidirectional ephrin/Eph signaling in synaptic functions.Brain Res. 2007 Dec 12;1184:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.11.033. Epub 2006 Dec 12. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17166489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular and trans-synaptic regulation of glutamatergic synaptogenesis by EphB receptors.J Neurosci. 2006 Nov 22;26(47):12152-64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3072-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17122040 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Extracellular matrix control of dendritic spine and synapse structure and plasticity in adulthood.Front Neuroanat. 2014 Oct 20;8:116. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2014.00116. eCollection 2014. Front Neuroanat. 2014. PMID: 25368556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Consequences of Synapse Remodeling Following Astrocyte-Specific Regulation of Ephrin-B1 in the Adult Hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2018 Jun 20;38(25):5710-5726. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3618-17.2018. Epub 2018 May 23. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29793972 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated Eph-ephrin signaling guides migration and axon targeting in the avian auditory system.Neural Dev. 2012 Aug 21;7:29. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-7-29. Neural Dev. 2012. PMID: 22908944 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic activation of EphB2 receptor in dendrites induced actin polymerization by activating Arg kinase.Biol Open. 2017 Dec 15;6(12):1820-1830. doi: 10.1242/bio.029900. Biol Open. 2017. PMID: 29158322 Free PMC article.
-
A delicate balance: role of MMP-9 in brain development and pathophysiology of neurodevelopmental disorders.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jul 29;9:280. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00280. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26283917 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hirai H, Maru Y, Hagiwara K, Nishida J, Takaku F. A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the eph gene. Science. 1987;238:1717–20. - PubMed
-
- Bartley TD, Hunt RW, Welcher AA, Boyle WJ, Parker VP, Lindberg RA, Lu HS, Colombero AM, Elliott RL, Guthrie BA, et al. B61 is a ligand for the ECK receptor protein-tyrosine kinase. Nature. 1994;368:558–60. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho RF, Beutler M, Marler KJM, Knöll B, Becker-Barroso E, Heintzmann R, Ng T, Drescher U. Silencing of EphA3 through a cis interaction with ephrinA5. Nature Neurosci. 2006;9(3):322–30. - PubMed
-
- Eph Nomenclature Committee. Unified nomenclature for Eph family receptors and their ligands, the ephrins. Cell. 1997;90:403–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

