Discovery of β-arrestin-biased dopamine D2 ligands for probing signal transduction pathways essential for antipsychotic efficacy
- PMID: 22025698
- PMCID: PMC3215024
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1104807108
Discovery of β-arrestin-biased dopamine D2 ligands for probing signal transduction pathways essential for antipsychotic efficacy
Abstract
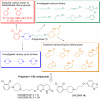
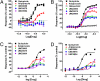
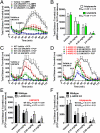
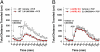
Elucidating the key signal transduction pathways essential for both antipsychotic efficacy and side-effect profiles is essential for developing safer and more effective therapies. Recent work has highlighted noncanonical modes of dopamine D(2) receptor (D(2)R) signaling via β-arrestins as being important for the therapeutic actions of both antipsychotic and antimanic agents. We thus sought to create unique D(2)R agonists that display signaling bias via β-arrestin-ergic signaling. Through a robust diversity-oriented modification of the scaffold represented by aripiprazole (1), we discovered UNC9975 (2), UNC0006 (3), and UNC9994 (4) as unprecedented β-arrestin-biased D(2)R ligands. These compounds also represent unprecedented β-arrestin-biased ligands for a G(i)-coupled G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). Significantly, UNC9975, UNC0006, and UNC9994 are simultaneously antagonists of G(i)-regulated cAMP production and partial agonists for D(2)R/β-arrestin-2 interactions. Importantly, UNC9975 displayed potent antipsychotic-like activity without inducing motoric side effects in inbred C57BL/6 mice in vivo. Genetic deletion of β-arrestin-2 simultaneously attenuated the antipsychotic actions of UNC9975 and transformed it into a typical antipsychotic drug with a high propensity to induce catalepsy. Similarly, the antipsychotic-like activity displayed by UNC9994, an extremely β-arrestin-biased D(2)R agonist, in wild-type mice was completely abolished in β-arrestin-2 knockout mice. Taken together, our results suggest that β-arrestin signaling and recruitment can be simultaneously a significant contributor to antipsychotic efficacy and protective against motoric side effects. These functionally selective, β-arrestin-biased D(2)R ligands represent valuable chemical probes for further investigations of D(2)R signaling in health and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure-functional selectivity relationship studies of β-arrestin-biased dopamine D₂ receptor agonists.J Med Chem. 2012 Aug 23;55(16):7141-53. doi: 10.1021/jm300603y. Epub 2012 Aug 13. J Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22845053 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of β-Arrestin-Biased Dopamine D2 Receptor Ligands on Schizophrenia-Like Behavior in Hypoglutamatergic Mice.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Feb;41(3):704-15. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.196. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26129680 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonism of dopamine D2 receptor/beta-arrestin 2 interaction is a common property of clinically effective antipsychotics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 9;105(36):13656-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803522105. Epub 2008 Sep 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18768802 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo veritas, the next frontier for functionally selective GPCR ligands.Methods. 2016 Jan 1;92:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.08.018. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Methods. 2016. PMID: 26320830 Review.
-
New Concepts in Dopamine D2 Receptor Biased Signaling and Implications for Schizophrenia Therapy.Biol Psychiatry. 2017 Jan 1;81(1):78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.10.011. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Biol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 27832841 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential In Vitro Pharmacological Profiles of Structurally Diverse Nociceptin Receptor Agonists in Activating G Protein and Beta-Arrestin Signaling at the Human Nociceptin Opioid Receptor.Mol Pharmacol. 2021 Jul;100(1):7-18. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.120.000076. Epub 2021 May 6. Mol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33958480 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted functions of β-arrestins and their therapeutic potential in neurodegenerative diseases.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Feb;56(1):129-141. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01144-4. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38212557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single Amino Acid Variation Underlies Species-Specific Sensitivity to Amphibian Skin-Derived Opioid-like Peptides.Chem Biol. 2015 Jun 18;22(6):764-75. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.05.012. Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 26091169 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescent ligands: Bringing light to emerging GPCR paradigms.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Mar;177(5):978-991. doi: 10.1111/bph.14953. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31877233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The histamine H3 receptor modulates dopamine D2 receptor-dependent signaling pathways and mouse behaviors.J Biol Chem. 2023 Apr;299(4):104583. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104583. Epub 2023 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36871761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luttrell LM, et al. Beta-arrestin-dependent formation of beta2 adrenergic receptor-Src protein kinase complexes. Science. 1999;283:655–661. - PubMed
-
- Lefkowitz RJ, Shenoy SK. Transduction of receptor signals by beta-arrestins. Science. 2005;308:512–517. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu JM, et al. An Akt/beta-arrestin 2/PP2A signaling complex mediates dopaminergic neurotransmission and behavior. Cell. 2005;122:261–273. - PubMed
-
- Urban JD, et al. Functional selectivity and classical concepts of quantitative pharmacology. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;320:1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

