Circulating cytokine levels, Epstein-Barr viremia, and risk of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 22022727
- PMCID: PMC3320652
- DOI: 10.1002/ajh.22119
Circulating cytokine levels, Epstein-Barr viremia, and risk of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
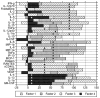
Cytokine dysregulation and decontrol of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latency by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection are potential mechanisms for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). We therefore assessed circulating blood levels in pre-diagnosis plasma or serum from 63 AIDS-related NHL cases 0.1 – 2.0 (median 1.0) years pre-NHL and 181 controls matched for CD4+ T-cell count. Cytokines were measured by Millipore 30-plex Luminex assays and cell-free EBV DNA detected by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Correlations in multiplex cytokine levels were summarized by factor analysis. Individual cytokines and their principal factors were analyzed for associations with NHL by conditional logistic regression. Cases had higher levels for 25 of the 30 cytokines. In analyses of cytokine profiles, cases had significantly higher scores for a principal factor primarily reflecting levels of interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5, IL-13, and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (four gene products with coordinated transcription in vitro), as well as IL-1alpha. Epstein-Barr viremia was not significantly associated based on 113 evaluable samples without PCR inhibition. We found increases of T-helper type 2 interleukins and generalized elevations of other inflammatory cytokines and growth factors up to two years before AIDS-NHL. Cytokine-mediated hyperstimulation of B-cell proliferation may play a role in AIDS-related lymphomagenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Absolute level of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection is not predictive of AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma.J Infect Dis. 2002 Aug 1;186(3):405-9. doi: 10.1086/341460. Epub 2002 Jul 17. J Infect Dis. 2002. PMID: 12134237
-
A longitudinal and prospective study of Epstein-Barr virus load in AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma.J Clin Virol. 2006 Aug;36(4):258-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2006.04.005. Epub 2006 Jun 9. J Clin Virol. 2006. PMID: 16762591
-
Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of patients with AIDS-related lymphoma.J Neurovirol. 2002 Oct;8(5):432-8. doi: 10.1080/13550280260422730. J Neurovirol. 2002. PMID: 12402169
-
The impact of EBV and HIV infection on the microenvironmental niche underlying Hodgkin lymphoma pathogenesis.Int J Cancer. 2017 Mar 15;140(6):1233-1245. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30473. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Int J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27750386 Review.
-
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related systemic non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.Br J Haematol. 2001 Mar;112(4):863-73. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02654.x. Br J Haematol. 2001. PMID: 11298581 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Human herpesvirus-encoded kinase induces B cell lymphomas in vivo.J Clin Invest. 2018 Jun 1;128(6):2519-2534. doi: 10.1172/JCI97053. Epub 2018 May 7. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 29733294 Free PMC article.
-
Coxiella burnetii antibody seropositivity is not a risk factor for AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma.Blood. 2017 Jun 15;129(24):3262-3264. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-12-756569. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28396496 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. No abstract available.
-
Serum levels of cytokines and biomarkers for inflammation and immune activation, and HIV-associated non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma risk.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014 Feb;23(2):343-9. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-13-0714. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014. PMID: 24220912 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment circulating serum cytokines associated with follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a clinic-based case-control study.Cytokine. 2012 Dec;60(3):882-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.08.028. Epub 2012 Sep 23. Cytokine. 2012. PMID: 23010502 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic approaches to investigate gammaherpesvirus biology and associated tumorigenesis.Adv Virus Res. 2021;109:201-254. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2020.10.001. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Adv Virus Res. 2021. PMID: 33934828 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Khaled AR, Durum SK. The role of cytokines in lymphocyte homeostasis. Biotechniques. 2002;(Suppl):40–45. - PubMed
-
- Goedert JJ, Sarngadharan MG, Biggar RJ, et al. Determinants of retrovirus (HTLV-III) antibody and immunodeficiency conditions in homosexual men. Lancet. 1984;2:711–716. - PubMed
-
- Goedert JJ, Kessler CM, Aledort LM, et al. A prospective study of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection and the development of AIDS in subjects with hemophilia. NEnglJMed. 1989;321:1141–1148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials