The lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1 promotes epithelial cell apoptosis after lung injury
- PMID: 22021336
- PMCID: PMC3326436
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0155OC
The lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1 promotes epithelial cell apoptosis after lung injury
Abstract
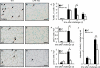
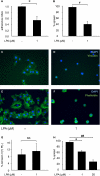
Increased epithelial cell apoptosis in response to lung injury has been implicated in the development of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), but the molecular pathways promoting epithelial cell apoptosis in this disease have yet to be fully identified. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), which we have previously demonstrated to mediate bleomycin lung injury-induced fibroblast recruitment and vascular leak in mice and fibroblast recruitment in patients with IPF, is an important regulator of survival and apoptosis in many cell types. We now show that LPA signaling through its receptor LPA(1) promotes epithelial cell apoptosis induced by bleomycin injury. The number of apoptotic cells present in the alveolar and bronchial epithelia of LPA(1)-deficient mice was significantly reduced compared with wild-type mice at Day 3 after bleomycin challenge, as was lung caspase-3 activity. Consistent with these in vivo results, we found that LPA signaling through LPA(1) induced apoptosis in normal human bronchial epithelial cells in culture. LPA-LPA(1) signaling appeared to specifically mediate anoikis, the apoptosis of anchorage-dependent cells induced by their detachment. Similarly, LPA negatively regulated attachment of R3/1 rat alveolar epithelial cell line cells. In contrast, LPA signaling through LPA(1) promoted the resistance of lung fibroblasts to apoptosis, which has also been implicated in IPF. The ability of LPA-LPA(1) signaling to promote epithelial cell apoptosis and fibroblast resistance to apoptosis may therefore contribute to the capacity of this signaling pathway to regulate the development of pulmonary fibrosis after lung injury.
Figures

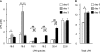
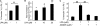
Similar articles
-
Lysophosphatidic acid receptor-2 deficiency confers protection against bleomycin-induced lung injury and fibrosis in mice.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Dec;49(6):912-22. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0070OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23808384 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophosphatidic acid signaling through its receptor initiates profibrotic epithelial cell fibroblast communication mediated by epithelial cell derived connective tissue growth factor.Kidney Int. 2017 Mar;91(3):628-641. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.09.030. Epub 2016 Dec 4. Kidney Int. 2017. PMID: 27927603 Free PMC article.
-
The lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1 links pulmonary fibrosis to lung injury by mediating fibroblast recruitment and vascular leak.Nat Med. 2008 Jan;14(1):45-54. doi: 10.1038/nm1685. Epub 2007 Dec 9. Nat Med. 2008. PMID: 18066075
-
Role of the lysophospholipid mediators lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phosphate in lung fibrosis.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2012 Jul;9(3):102-10. doi: 10.1513/pats.201201-005AW. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2012. PMID: 22802282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced lung injury in animals and its applicability to human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Exp Lung Res. 2015 Mar;41(2):57-73. doi: 10.3109/01902148.2014.979516. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Exp Lung Res. 2015. PMID: 25514507 Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular interactions in the pathogenesis of interstitial lung diseases.Eur Respir Rev. 2015 Mar;24(135):102-14. doi: 10.1183/09059180.00003214. Eur Respir Rev. 2015. PMID: 25726561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysophosphatidic Acid Signaling through the Lysophosphatidic Acid-1 Receptor Is Required for Alveolarization.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016 Jul;55(1):105-16. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2015-0152OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27082727 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptors: Biochemical and Clinical Implications in Different Diseases.J Cancer. 2020 Mar 15;11(12):3519-3535. doi: 10.7150/jca.41841. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32284748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone Marrow-Derived Mononuclear Cell Therapy in Papain-Induced Experimental Pulmonary Emphysema.Front Physiol. 2018 Feb 20;9:121. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00121. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29515461 Free PMC article.
-
Ziritaxestat, a Novel Autotaxin Inhibitor, and Lung Function in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: The ISABELA 1 and 2 Randomized Clinical Trials.JAMA. 2023 May 9;329(18):1567-1578. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.5355. JAMA. 2023. PMID: 37159034 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Selman M, King TE, Pardo A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Prevailing and evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for therapy. Ann Intern Med 2001;134:136–151 - PubMed
-
- Tager AM, LaCamera P, Shea BS, Campanella GS, Selman M, Zhao Z, Polosukhin V, Wain J, Karimi-Shah BA, Kim ND, et al. The lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA1 links pulmonary fibrosis to lung injury by mediating fibroblast recruitment and vascular leak. Nat Med 2008;14:45–54 - PubMed
-
- Choi JW, Herr DR, Noguchi K, Yung YC, Lee CW, Mutoh T, Lin ME, Teo ST, Park KE, Mosley AN, et al. LPA receptors: subtypes and biological actions. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2010;50:157–186 - PubMed
-
- Ye X, Ishii I, Kingsbury MA, Chun J. Lysophosphatidic acid as a novel cell survival/apoptotic factor. Biochim Biophys Acta 2002;1585:108–113 - PubMed
-
- Kuwano K, Kunitake R, Kawasaki M, Nomoto Y, Hagimoto N, Nakanishi Y, Hara N. P21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1 and p53 expression in association with DNA strand breaks in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996;154:477–483 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

