Contributions of the Epstein-Barr virus EBNA1 protein to gastric carcinoma
- PMID: 22013060
- PMCID: PMC3255905
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.05623-11
Contributions of the Epstein-Barr virus EBNA1 protein to gastric carcinoma
Abstract
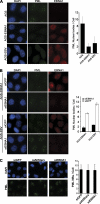
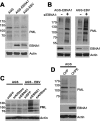
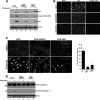
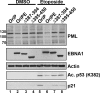
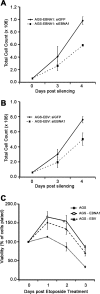
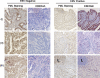
Approximately 10% of gastric carcinomas (GC) are comprised of cells latently infected with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV); however, the mechanism by which EBV contributes to the development of this malignancy is unclear. We have investigated the cellular effects of the only EBV nuclear protein expressed in GC, EBNA1, focusing on promyelocytic leukemia (PML) nuclear bodies (NBs), which play important roles in apoptosis, p53 activation, and tumor suppression. AGS GC cells infected with EBV were found to contain fewer PML NBs and less PML protein than the parental EBV-negative AGS cells, and these levels were restored by silencing EBNA1. Conversely, EBNA1 expression was sufficient to induce the loss of PML NBs and proteins in AGS cells. Consistent with PML functions, EBNA1 expression decreased p53 activation and apoptosis in response to DNA damage and resulted in increased cell survival. In addition, EBNA1 mutants unable to bind CK2 kinase or ubiquitin-specific protease 7 had decreased ability to induce PML loss and to interfere with p53 activation. PML levels in EBV-positive and EBV-negative GC biopsy specimens were then compared by immunohistochemistry. Consistent with the results in the AGS cells, EBV-positive tumors had significantly lower PML levels than EBV-negative tumors. The results indicate that EBV infection of GC cells leads to loss of PML NBs through the action of EBNA1, resulting in impaired responses to DNA damage and promotion of cell survival. Therefore, PML disruption by EBNA1 is one mechanism by which EBV may contribute to the development of gastric cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 contributes to nasopharyngeal carcinoma through disruption of PML nuclear bodies.PLoS Pathog. 2008 Oct 3;4(10):e1000170. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000170. PLoS Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18833293 Free PMC article.
-
Viral disruption of promyelocytic leukemia (PML) nuclear bodies by hijacking host PML regulators.Virulence. 2011 Jan-Feb;2(1):58-62. doi: 10.4161/viru.2.1.14610. Epub 2011 Jan 1. Virulence. 2011. PMID: 21217204
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 Hijacks the host kinase CK2 to disrupt PML nuclear bodies.J Virol. 2010 Nov;84(21):11113-23. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01183-10. Epub 2010 Aug 18. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20719947 Free PMC article.
-
Potential cellular functions of Epstein-Barr Nuclear Antigen 1 (EBNA1) of Epstein-Barr Virus.Viruses. 2013 Jan 16;5(1):226-40. doi: 10.3390/v5010226. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23325328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EBNA1.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:3-34. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_1. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428370 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of Epstein-Barr virus infection in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Virol Sin. 2015 Apr;30(2):107-21. doi: 10.1007/s12250-015-3592-5. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Virol Sin. 2015. PMID: 25910483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contributions of Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) to cell immortalization and survival.Viruses. 2012 Sep;4(9):1537-1547. doi: 10.3390/v4091537. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23170171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Kinase CK2 and Epstein-Barr Virus.Biomedicines. 2023 Jan 26;11(2):358. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020358. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36830895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Similarities between the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Nuclear Protein EBNA1 and the Pioneer Transcription Factor FoxA: Is EBNA1 a "Bookmarking" Oncoprotein that Alters the Host Cell Epigenotype?Pathogens. 2012 Sep 17;1(1):37-51. doi: 10.3390/pathogens1010037. Pathogens. 2012. PMID: 25436603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral Oncology: Molecular Biology and Pathogenesis.J Clin Med. 2017 Nov 29;6(12):111. doi: 10.3390/jcm6120111. J Clin Med. 2017. PMID: 29186062 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bernardi R, Pandolfi PP. 2007. Structure, dynamics and functions of promyelocytic leukaemia nuclear bodies. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8:1006–1016 - PubMed
-
- Catalano V, et al. 2009. Gastric cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 71:127–164 - PubMed
-
- Cheng TC, et al. 2010. Expression of Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 in gastric carcinoma cells is associated with enhanced tumorigenicity and reduced cisplatin sensitivity. Int. J. Oncol. 36:151–160 - PubMed
-
- de Stanchina E, et al. 2004. PML is a direct p53 target that modulates p53 effector functions. Mol. Cell 13:523–535 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

