Targeted entry via somatostatin receptors using a novel modified retrovirus glycoprotein that delivers genes at levels comparable to those of wild-type viral glycoproteins
- PMID: 22013043
- PMCID: PMC3255891
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.05411-11
Targeted entry via somatostatin receptors using a novel modified retrovirus glycoprotein that delivers genes at levels comparable to those of wild-type viral glycoproteins
Abstract
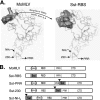
Here we report a novel viral glycoprotein created by replacing a natural receptor-binding sequence of the ecotropic Moloney murine leukemia virus envelope glycoprotein with the peptide ligand somatostatin. This new chimeric glycoprotein, which has been named the Sst receptor binding site (Sst-RBS), gives targeted transduction based on three criteria: (i) a gain of the use of a new entry receptor not used by any known virus; (ii) targeted entry at levels comparable to gene delivery by wild-type ecotropic Moloney murine leukemia virus and vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) G glycoproteins; and (iii) a loss of the use of the natural ecotropic virus receptor. Retroviral vectors coated with Sst-RBS gained the ability to bind and transduce human 293 cells expressing somatostatin receptors. Their infection was specific to target somatostatin receptors, since a synthetic somatostatin peptide inhibited infection in a dose-dependent manner and the ability to transduce mouse cells bearing the natural ecotropic receptor was effectively lost. Importantly, vectors coated with the Sst-RBS glycoprotein gave targeted entry of up to 1 × 10(6) transducing U/ml, a level comparable to that seen with infection of vectors coated with the parental wild-type ecotropic Moloney murine leukemia virus glycoprotein through the ecotropic receptor and approaching that of infection of VSV G-coated vectors through the VSV receptor. To our knowledge, this is the first example of a glycoprotein that gives targeted entry of retroviral vectors at levels comparable to the natural capacity of viral envelope glycoproteins.
Figures

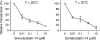
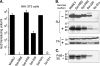

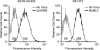
Similar articles
-
Identification of regions in the Moloney murine leukemia virus SU protein that tolerate the insertion of an integrin-binding peptide.Virology. 2000 Mar 30;269(1):7-17. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0201. Virology. 2000. PMID: 10725193
-
A hydrophobic patch in ecotropic murine leukemia virus envelope protein is the putative binding site for a critical tyrosine residue on the cellular receptor.J Virol. 1999 Dec;73(12):10164-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.10164-10172.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10559332 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudotransduction of hepatocytes by using concentrated pseudotyped vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein (VSV-G)-Moloney murine leukemia virus-derived retrovirus vectors: comparison of VSV-G and amphotropic vectors for hepatic gene transfer.J Virol. 1996 Apr;70(4):2497-502. doi: 10.1128/JVI.70.4.2497-2502.1996. J Virol. 1996. PMID: 8642678 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of high-titer pseudotyped retroviral vectors with very broad host range.Methods Cell Biol. 1994;43 Pt A:99-112. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60600-7. Methods Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 7823872 Review.
-
Cell targeting by murine recombinant retroviruses.Bone Marrow Transplant. 1992;9 Suppl 1:139-42. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1992. PMID: 1504656 Review.
Cited by
-
Directed Molecular Evolution of an Engineered Gammaretroviral Envelope Protein with Dual Receptor Use Shows Stable Maintenance of Both Receptor Specificities.J Virol. 2015 Nov 25;90(3):1647-56. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02013-15. Print 2016 Feb 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26608314 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of the cellular receptor influence the intracellular fate and efficiency of virus infection.J Virol. 2013 May;87(10):5916-25. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00398-13. Epub 2013 Mar 20. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23514894 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic investigation of neural circuits underlying brain disease in animal models.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012 Mar 20;13(4):251-66. doi: 10.1038/nrn3171. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22430017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Receptor-Ligand Interaction in Somatostatin Signaling Pathways: Implications for Neuroendocrine Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 25;16(1):116. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010116. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38201544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Library screening and receptor-directed targeting of gammaretroviral vectors.Future Microbiol. 2013 Jan;8(1):107-21. doi: 10.2217/fmb.12.122. Future Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23252496 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albritton LM, Tseng L, Scadden D, Cunningham JM. 1989. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell 57:659–666 - PubMed
-
- Anderson WF. 1998. Human gene therapy. Nature 392:25–30 - PubMed
-
- Anliker B, et al. 2010. Specific gene transfer to neurons, endothelial cells and hematopoietic progenitors with lentiviral vectors. Nat. Methods 7:929–935 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

