The small molecule TGF-β signaling inhibitor SM16 synergizes with agonistic OX40 antibody to suppress established mammary tumors and reduce spontaneous metastasis
- PMID: 21971588
- PMCID: PMC3595193
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-011-1119-y
The small molecule TGF-β signaling inhibitor SM16 synergizes with agonistic OX40 antibody to suppress established mammary tumors and reduce spontaneous metastasis
Abstract
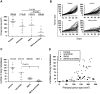
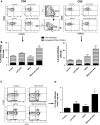
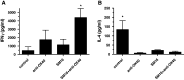
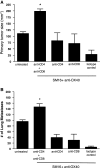
Effective tumor immunotherapy may require not only activation of anti-tumor effector cells, but also abrogation of tumor-mediated immunosuppression. The cytokine TGF-β, is frequently elevated in the tumor microenvironment and is a potent immunosuppressive agent and promoter of tumor metastasis. OX40 (CD134) is a member of the TNF-α receptor superfamily and ligation by agonistic antibody (anti-OX40) enhances effector function, expansion, and survival of activated T cells. In this study, we examined the therapeutic efficacy and anti-tumor immune response induced by the combination of a small molecule TGF-β signaling inhibitor, SM16, plus anti-OX40 in the poorly immunogenic, highly metastatic, TGF-β-secreting 4T1 mammary tumor model. Our data show that SM16 and anti-OX40 mutually enhanced each other to elicit a potent anti-tumor effect against established primary tumors, with a 79% reduction in tumor size, a 95% reduction in the number of metastatic lung nodules, and a cure rate of 38%. This positive treatment outcome was associated with a 3.2-fold increase of tumor-infiltrating, activated CD8+ T cells, an overall accumulation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and an increased tumor-specific effector T cell response. Complete abrogation of the therapeutic effect in vivo following depletion of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells suggests that the anti-tumor efficacy of SM16+ anti-OX40 therapy is T cell dependent. Mice that were cured of their tumors were able to reject tumor re-challenge and manifested a significant tumor-specific peripheral memory IFN-γ response. Taken together, these data suggest that combining a TGF-β signaling inhibitor with anti-OX40 is a viable approach for treating metastatic breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An orally active small molecule TGF-beta receptor I antagonist inhibits the growth of metastatic murine breast cancer.Anticancer Res. 2009 Jun;29(6):2099-109. Anticancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19528470 Free PMC article.
-
STAT3 Signaling Is Required for Optimal Regression of Large Established Tumors in Mice Treated with Anti-OX40 and TGFβ Receptor Blockade.Cancer Immunol Res. 2015 May;3(5):526-35. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0187. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 25627655
-
PD-1 blockade and OX40 triggering synergistically protects against tumor growth in a murine model of ovarian cancer.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 27;9(2):e89350. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089350. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586709 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling through OX40 enhances antitumor immunity.Semin Oncol. 2010 Oct;37(5):524-32. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2010.09.013. Semin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 21074068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Science gone translational: the OX40 agonist story.Immunol Rev. 2011 Nov;244(1):218-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01069.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 22017441 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The roles of TGFβ in the tumour microenvironment.Nat Rev Cancer. 2013 Nov;13(11):788-99. doi: 10.1038/nrc3603. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24132110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intratumoral immunotherapy with mRNAs encoding chimeric protein constructs encompassing IL-12, CD137 agonists, and TGF-β antagonists.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023 Jul 28;33:668-682. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.07.026. eCollection 2023 Sep 12. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023. PMID: 37650116 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic vaccines for cancer: an overview of clinical trials.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014 Sep;11(9):509-24. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.111. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25001465 Review.
-
Targeting small molecule drugs to T cells with antibody-directed cell-penetrating gold nanoparticles.Biomater Sci. 2018 Dec 18;7(1):113-124. doi: 10.1039/c8bm01208c. Biomater Sci. 2018. PMID: 30444251 Free PMC article.
-
CD73 expression on effector T cells sustained by TGF-β facilitates tumor resistance to anti-4-1BB/CD137 therapy.Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 11;10(1):150. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08123-8. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30635578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellone G, Turletti A, Artusio E, Mareschi K, Carbone A, Tibaudi D, Robecchi A, Emanuelli G, Rodeck U. Tumor-associated transforming growth factor-beta and interleukin-10 contribute to a systemic Th2 immune phenotype in pancreatic carcinoma patients. Am J Pathol. 1999;155(2):537–547. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65149-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shim KS, Kim KH, Han WS, Park EB. Elevated serum levels of transforming growth factor-beta1 in patients with colorectal carcinoma: its association with tumor progression and its significant decrease after curative surgical resection. Cancer. 1999;85(3):554–561. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19990201)85:3<554::AID-CNCR6>3.0.CO;2-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

