A conserved regulatory role for antisense RNA in meiotic gene expression in yeast
- PMID: 21963111
- PMCID: PMC3230709
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2011.09.010
A conserved regulatory role for antisense RNA in meiotic gene expression in yeast
Abstract
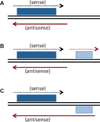
A significant fraction of the eukaryotic genome is transcribed into RNAs that do not encode proteins, termed non-coding RNA (ncRNA). One class of ncRNA that is of particular interest is antisense RNAs, which are complementary to protein coding transcripts (mRNAs). In this article, we summarize recent studies using different yeasts that reveal a conserved pattern in which meiotically expressed genes have antisense transcripts in vegetative cells. These antisense transcripts repress the basal transcription of the mRNA during vegetative growth and are diminished as cells enter meiosis. While the mechanism(s) by which these antisense RNAs interfere with production of sense transcripts is not yet understood, the effects appear to be independent of the canonical RNAi machinery.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
XUTs are a class of Xrn1-sensitive antisense regulatory non-coding RNA in yeast.Nature. 2011 Jun 22;475(7354):114-7. doi: 10.1038/nature10118. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21697827
-
Antisense transcription controls cell fate in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Cell. 2006 Nov 17;127(4):735-45. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.038. Cell. 2006. PMID: 17110333
-
An antisense RNA-mediated mechanism eliminates a meiosis-specific copper-regulated transcript in mitotic cells.J Biol Chem. 2015 Sep 11;290(37):22622-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.674556. Epub 2015 Jul 30. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26229103 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense gene expression in yeast.Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1994 Nov;375(11):721-9. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1994.375.11.721. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1994. PMID: 7695834 Review.
-
Natural antisense transcripts: sound or silence?Physiol Genomics. 2005 Oct 17;23(2):125-31. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00124.2005. Physiol Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16230481 Review.
Cited by
-
Species and condition specific adaptation of the transcriptional landscapes in Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis.BMC Genomics. 2013 Apr 2;14:212. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-212. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23547856 Free PMC article.
-
Ustilago maydis natural antisense transcript expression alters mRNA stability and pathogenesis.Mol Microbiol. 2013 Jul;89(1):29-51. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12254. Epub 2013 May 30. Mol Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23650872 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of RNA targets for the nuclear multidomain cyclophilin atCyp59 and their effect on PPIase activity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Feb 1;41(3):1783-96. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1252. Epub 2012 Dec 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23248006 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved expression of natural antisense transcripts in mammals.BMC Genomics. 2013 Apr 12;14:243. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-243. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23577827 Free PMC article.
-
BRG1 and NRG1 form a novel feedback circuit regulating Candida albicans hypha formation and virulence.Mol Microbiol. 2012 Aug;85(3):557-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08127.x. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Mol Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22757963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakamura T, Kishida M, Shimoda C. The Schizosaccharomyces pombe spo6+ gene encoding a nuclear protein with sequence similarity to budding yeast Dbf4 is required for meiotic second division and sporulation. Genes Cells. 2000;5:463–479. - PubMed
-
- Hongay CF, Grisafi PL, Galitski T, Fink GR. Antisense transcription controls cell fate in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 2006;127:735–745. - PubMed
-
-
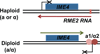
Gelfand B, Mead J, Bruning A, Apostolopoulos N, Tadigotla V, Nagaraj V, Sengupta AM, Vershon AK. Regulated antisense transcription controls expression of cell-type specific genes in yeast. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31:1701–1709. Analysis of the sense/antisense pair
IME4/RME2 indicates thatRME2 interferes withIME4 expression by inhibiting elongation rather than inititation of the sense transcript.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

