Deficiency of CRTAP in non-lethal recessive osteogenesis imperfecta reduces collagen deposition into matrix
- PMID: 21955071
- PMCID: PMC3748815
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2011.01794.x
Deficiency of CRTAP in non-lethal recessive osteogenesis imperfecta reduces collagen deposition into matrix
Abstract
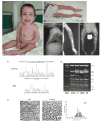
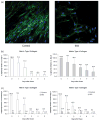
Deficiency of any component of the ER-resident collagen prolyl 3-hydroxylation complex causes recessive osteogenesis imperfecta (OI). The complex modifies the α1(I)Pro986 residue and contains cartilage-associated protein (CRTAP), prolyl 3-hydroxylase 1 (P3H1) and cyclophilin B (CyPB). Fibroblasts normally secrete about 10% of CRTAP. Most CRTAP mutations cause a null allele and lethal type VII OI. We identified a 7-year-old Egyptian boy with non-lethal type VII OI and investigated the effects of his null CRTAP mutation on collagen biochemistry, the prolyl 3-hydroxylation complex, and collagen in extracellular matrix. The proband is homozygous for an insertion/deletion in CRTAP (c.118_133del16insTACCC). His dermal fibroblasts synthesize fully overmodified type I collagen, and 3-hydroxylate only 5% of α1(I)Pro986. CRTAP transcripts are 10% of control. CRTAP protein is absent from proband cells, with residual P3H1 and normal CyPB levels. Dermal collagen fibril diameters are significantly increased. By immunofluorescence of long-term cultures, we identified a severe deficiency (10-15% of control) of collagen deposited in extracellular matrix, with disorganization of the minimal fibrillar network. Quantitative pulse-chase experiments corroborate deficiency of matrix deposition, rather than increased matrix turnover. We conclude that defects of extracellular matrix, as well as intracellular defects in collagen modification, contribute to the pathology of type VII OI.
© 2011 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prolyl 3-hydroxylase 1 and CRTAP are mutually stabilizing in the endoplasmic reticulum collagen prolyl 3-hydroxylation complex.Hum Mol Genet. 2010 Jan 15;19(2):223-34. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp481. Epub 2009 Oct 21. Hum Mol Genet. 2010. PMID: 19846465 Free PMC article.
-
Null mutations in LEPRE1 and CRTAP cause severe recessive osteogenesis imperfecta.Cell Tissue Res. 2010 Jan;339(1):59-70. doi: 10.1007/s00441-009-0872-0. Epub 2009 Oct 28. Cell Tissue Res. 2010. PMID: 19862557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutations in PPIB (cyclophilin B) delay type I procollagen chain association and result in perinatal lethal to moderate osteogenesis imperfecta phenotypes.Hum Mol Genet. 2011 Apr 15;20(8):1595-609. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr037. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Hum Mol Genet. 2011. PMID: 21282188 Free PMC article.
-
Recessive osteogenesis imperfecta caused by LEPRE1 mutations: clinical documentation and identification of the splice form responsible for prolyl 3-hydroxylation.J Med Genet. 2009 Apr;46(4):233-41. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2008.062729. Epub 2008 Dec 16. J Med Genet. 2009. PMID: 19088120
-
Components of the collagen prolyl 3-hydroxylation complex are crucial for normal bone development.Cell Cycle. 2007 Jul 15;6(14):1675-81. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.14.4474. Epub 2007 May 18. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17630507 Review.
Cited by
-
On the association between Chiari malformation type 1, bone mineral density and bone related genes.Bone Rep. 2022 Mar 15;16:101181. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2022.101181. eCollection 2022 Jun. Bone Rep. 2022. PMID: 35313637 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular stress due to impairment of collagen prolyl hydroxylation complex is rescued by the chaperone 4-phenylbutyrate.Dis Model Mech. 2019 Jun 20;12(6):dmm038521. doi: 10.1242/dmm.038521. Dis Model Mech. 2019. PMID: 31171565 Free PMC article.
-
Osteogenesis imperfecta and therapeutics.Matrix Biol. 2018 Oct;71-72:294-312. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.03.010. Epub 2018 Mar 11. Matrix Biol. 2018. PMID: 29540309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneity in proline hydroxylation of fibrillar collagens observed by mass spectrometry.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 31;16(8):e0250544. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250544. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34464391 Free PMC article.
-
Over-Representation of Recessive Osteogenesis Imperfecta in Asian Indian Children.J Pediatr Genet. 2020 Sep 16;11(1):81-86. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1716830. eCollection 2022 Mar. J Pediatr Genet. 2020. PMID: 35186396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Byers PH, Cole WG. Connective tissue and its heritable disorders. In: Royce PM, Steinmann B, editors. Osteogenesis imperfecta. New York, NY: Wiley-Liss, Inc.; 2002. pp. 385–430.
-
- Marini JC, Cabral WA, Barnes AM, Chang W. Components of the collagen prolyl 3-hydroxylation complex are crucial for normal bone development. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:1675–1681. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

