Specific control of pancreatic endocrine β- and δ-cell mass by class IIa histone deacetylases HDAC4, HDAC5, and HDAC9
- PMID: 21953612
- PMCID: PMC3198089
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-0440
Specific control of pancreatic endocrine β- and δ-cell mass by class IIa histone deacetylases HDAC4, HDAC5, and HDAC9
Abstract
Objective: Class IIa histone deacetylases (HDACs) belong to a large family of enzymes involved in protein deacetylation and play a role in regulating gene expression and cell differentiation. Previously, we showed that HDAC inhibitors modify the timing and determination of pancreatic cell fate. The aim of this study was to determine the role of class IIa HDACs in pancreas development.
Research design and methods: We took a genetic approach and analyzed the pancreatic phenotype of mice lacking HDAC4, -5, and -9. We also developed a novel method of lentiviral infection of pancreatic explants and performed gain-of-function experiments.
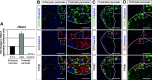
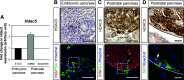
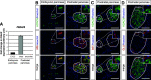
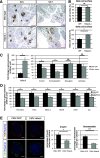
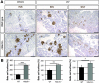
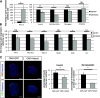
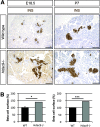
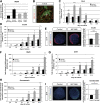
Results: We show that class IIa HDAC4, -5, and -9 have an unexpected restricted expression in the endocrine β- and δ-cells of the pancreas. Analyses of the pancreas of class IIa HDAC mutant mice revealed an increased pool of insulin-producing β-cells in Hdac5(-/-) and Hdac9(-/-) mice and an increased pool of somatostatin-producing δ-cells in Hdac4(-/-) and Hdac5(-/-) mice. Conversely, HDAC4 and HDAC5 overexpression showed a decreased pool of insulin-producing β-cells and somatostatin-producing δ-cells. Finally, treatment of pancreatic explants with the selective class IIa HDAC inhibitor MC1568 enhances expression of Pax4, a key factor required for proper β-and δ-cell differentiation and amplifies endocrine β- and δ-cells.
Conclusions: We conclude that HDAC4, -5, and -9 are key regulators to control the pancreatic β/δ-cell lineage. These results highlight the epigenetic mechanisms underlying the regulation of endocrine cell development and suggest new strategies for β-cell differentiation-based therapies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pax6 Inactivation in the Adult Pancreas Reveals Ghrelin as Endocrine Cell Maturation Marker.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 11;10(12):e0144597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144597. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26658466 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC4 and HDAC5 form a complex with DREAM that epigenetically down-regulates NCX3 gene and its pharmacological inhibition reduces neuronal stroke damage.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020 Oct;40(10):2081-2097. doi: 10.1177/0271678X19884742. Epub 2019 Nov 7. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020. PMID: 31696766 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase D1 mediates class IIa histone deacetylase phosphorylation and nuclear extrusion in intestinal epithelial cells: role in mitogenic signaling.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014 May 15;306(10):C961-71. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00048.2014. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24647541 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of class IIa HDAC activities: it is not only matter of subcellular localization.Epigenomics. 2016 Feb;8(2):251-69. doi: 10.2217/epi.15.106. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Epigenomics. 2016. PMID: 26791815 Review.
-
Class IIa HDACs - new insights into their functions in physiology and pathology.FEBS J. 2015 May;282(9):1736-44. doi: 10.1111/febs.13061. Epub 2014 Oct 27. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 25244360 Review.
Cited by
-
The Emerging Role of HDACs: Pathology and Therapeutic Targets in Diabetes Mellitus.Cells. 2021 May 28;10(6):1340. doi: 10.3390/cells10061340. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34071497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Human Islet: Mini-Organ With Mega-Impact.Endocr Rev. 2021 Sep 28;42(5):605-657. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnab010. Endocr Rev. 2021. PMID: 33844836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconstituting pancreas development from purified progenitor cells reveals genes essential for islet differentiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jul 30;110(31):12691-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1304507110. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23852729 Free PMC article.
-
Protein acetylation derepresses Serotonin Synthesis to potentiate Pancreatic Beta-Cell Function through HDAC1-PKA-Tph1 signaling.Theranostics. 2020 Jun 5;10(16):7351-7368. doi: 10.7150/thno.44459. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32641996 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Nutrient Intake during Pregnancy and Lactation on the Endocrine Pancreas of the Offspring.Nutrients. 2019 Nov 8;11(11):2708. doi: 10.3390/nu11112708. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31717308 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jonsson J, Carlsson L, Edlund T, Edlund H. Insulin-promoter-factor 1 is required for pancreas development in mice. Nature 1994;371:606–609 - PubMed
-
- Collombat P, Hecksher-Sørensen J, Serup P, Mansouri A. Specifying pancreatic endocrine cell fates. Mech Dev 2006;123:501–512 - PubMed
-
- Sosa-Pineda B, Chowdhury K, Torres M, Oliver G, Gruss P. The Pax4 gene is essential for differentiation of insulin-producing beta cells in the mammalian pancreas. Nature 1997;386:399–402 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

