Systemic administration of combinatorial dsiRNAs via nanoparticles efficiently suppresses HIV-1 infection in humanized mice
- PMID: 21952167
- PMCID: PMC3242666
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2011.207
Systemic administration of combinatorial dsiRNAs via nanoparticles efficiently suppresses HIV-1 infection in humanized mice
Abstract
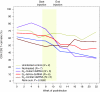
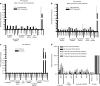
We evaluated the in vivo efficacy of structurally flexible, cationic PAMAM dendrimers as a small interfering RNA (siRNA) delivery system in a Rag2(-)/-γc-/- (RAG-hu) humanized mouse model for HIV-1 infection. HIV-infected humanized Rag2-/-γc-/- mice (RAG-hu) were injected intravenously (i.v.) with dendrimer-siRNA nanoparticles consisting of a cocktail of dicer substrate siRNAs (dsiRNAs) targeting both viral and cellular transcripts. We report in this study that the dendrimer-dsiRNA treatment suppressed HIV-1 infection by several orders of magnitude and protected against viral induced CD4(+) T-cell depletion. We also demonstrated that follow-up injections of the dendrimer-cocktailed dsiRNAs following viral rebound resulted in complete inhibition of HIV-1 titers. Biodistribution studies demonstrate that the dendrimer-dsiRNAs preferentially accumulate in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and liver and do not exhibit any discernable toxicity. These data demonstrate for the first time efficacious combinatorial delivery of anti-host and -viral siRNAs for HIV-1 treatment in vivo. The dendrimer delivery approach therefore represents a promising method for systemic delivery of combinations of siRNAs for treatment of HIV-1 infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Receptor-targeted aptamer-siRNA conjugate-directed transcriptional regulation of HIV-1.Theranostics. 2018 Feb 7;8(6):1575-1590. doi: 10.7150/thno.23085. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29556342 Free PMC article.
-
An aptamer-siRNA chimera suppresses HIV-1 viral loads and protects from helper CD4(+) T cell decline in humanized mice.Sci Transl Med. 2011 Jan 19;3(66):66ra6. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3001581. Sci Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21248316 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 infection and CD4 T cell depletion in the humanized Rag2-/-gamma c-/- (RAG-hu) mouse model.Retrovirology. 2006 Nov 1;3:76. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-3-76. Retrovirology. 2006. PMID: 17078891 Free PMC article.
-
Tat-Based Therapies as an Adjuvant for an HIV-1 Functional Cure.Viruses. 2020 Apr 8;12(4):415. doi: 10.3390/v12040415. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32276443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curing inflammatory diseases using phosphorous dendrimers.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022 Jul;14(4):e1783. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1783. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35194953 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiviral Stratagems Against HIV-1 Using RNA Interference (RNAi) Technology.Evol Bioinform Online. 2013 May 16;9:203-13. doi: 10.4137/EBO.S11412. Print 2013. Evol Bioinform Online. 2013. PMID: 23761954 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial anti-HIV gene therapy: using a multipronged approach to reach beyond HAART.Gene Ther. 2013 Jul;20(7):695-702. doi: 10.1038/gt.2012.98. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Gene Ther. 2013. PMID: 23364313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomaterial Strategies for Immunomodulation.Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2015;17:317-49. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071813-104814. Epub 2015 Sep 29. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2015. PMID: 26421896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-based TWIST1 inhibition via dendrimer complex to reduce breast cancer cell metastasis.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:382745. doi: 10.1155/2015/382745. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25759817 Free PMC article.
-
Nanostructures for the Inhibition of Viral Infections.Molecules. 2015 Aug 3;20(8):14051-81. doi: 10.3390/molecules200814051. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26247927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE., and, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
-
- Zamore PD, Tuschl T, Sharp PA., and, Bartel DP. RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell. 2000;101:25–33. - PubMed
-
- Kim DH., and, Rossi JJ. Strategies for silencing human disease using RNA interference. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:173–184. - PubMed
-
- Rossi JJ. RNAi as a treatment for HIV-1 infection. BioTechniques. 2006;Suppl:25–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

