A decade of exploring the cancer epigenome - biological and translational implications
- PMID: 21941284
- PMCID: PMC3307543
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc3130
A decade of exploring the cancer epigenome - biological and translational implications
Abstract
The past decade has highlighted the central role of epigenetic processes in cancer causation, progression and treatment. Next-generation sequencing is providing a window for visualizing the human epigenome and how it is altered in cancer. This view provides many surprises, including linking epigenetic abnormalities to mutations in genes that control DNA methylation, the packaging and the function of DNA in chromatin, and metabolism. Epigenetic alterations are leading candidates for the development of specific markers for cancer detection, diagnosis and prognosis. The enzymatic processes that control the epigenome present new opportunities for deriving therapeutic strategies designed to reverse transcriptional abnormalities that are inherent to the cancer epigenome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests. See Web version for details.
Figures
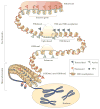

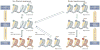

Similar articles
-
Compendium of aberrant DNA methylation and histone modifications in cancer.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Dec 5;455(1-2):3-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.08.140. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 25194808
-
Development-linked changes in DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation in humans: interview with Dr Melanie Ehrlich.Epigenomics. 2015 Aug;7(5):691-4. doi: 10.2217/epi.15.44. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Epigenomics. 2015. PMID: 26317371 No abstract available.
-
Targeting the cancer epigenome for therapy.Nat Rev Genet. 2016 Sep 15;17(10):630-41. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2016.93. Nat Rev Genet. 2016. PMID: 27629931 Review.
-
From 1957 to Nowadays: A Brief History of Epigenetics.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 14;21(20):7571. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207571. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33066397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmaco-epigenomics: On the Road of Translation Medicine.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1168:31-42. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-24100-1_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31713163 Review.
Cited by
-
Promoter Methylation of QKI as a Potential Specific Biomarker for Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 9;13:928150. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.928150. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36017498 Free PMC article.
-
The CREB Coactivator CRTC2 Is a Lymphoma Tumor Suppressor that Preserves Genome Integrity through Transcription of DNA Mismatch Repair Genes.Cell Rep. 2015 Jun 9;11(9):1350-7. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.04.052. Epub 2015 May 21. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26004186 Free PMC article.
-
EZH2 inhibition sensitizes BRG1 and EGFR mutant lung tumours to TopoII inhibitors.Nature. 2015 Apr 9;520(7546):239-42. doi: 10.1038/nature14122. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25629630 Free PMC article.
-
Only three driver gene mutations are required for the development of lung and colorectal cancers.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jan 6;112(1):118-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1421839112. Epub 2014 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25535351 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell function in atherosclerosis.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2013 May;15(5):319. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2013. PMID: 23630979 Review.
References
-
- Jones PA, Baylin SB. The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nature Rev Genet. 2002;3:415–428. - PubMed
-
- Allis C, Jenuwein T, Reinberg D. In: Epigenetics. Caparros M, editor. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2007.
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007;128:693–705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

