Targeting B cell responses in universal influenza vaccine design
- PMID: 21940217
- PMCID: PMC3212832
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2011.08.007
Targeting B cell responses in universal influenza vaccine design
Abstract
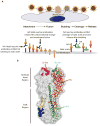
Since its first administration in the 1940s, the influenza vaccine has provided tremendous relief against influenza infections. However, time has revealed the ultimate limit of the vaccine and the call for its reinvention has now come, just as we are beginning to appreciate the antibody immune responses vital in preventing infections. New strategies to design the influenza vaccine rely on selectively inducing broadly neutralizing antibodies that are specific for highly conserved viral epitopes. Such approaches take us away from the limited range of protection provided by current seasonal influenza vaccines and towards a future with a pan-influenza vaccine capable of providing universal strain coverage.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heads, stalks and everything else: how can antibodies eradicate influenza as a human disease?Curr Opin Immunol. 2016 Oct;42:48-55. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2016.05.012. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27268395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influenza vaccination strategies targeting the hemagglutinin stem region.Immunol Rev. 2020 Jul;296(1):132-141. doi: 10.1111/imr.12887. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Immunol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32542739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is It Possible to Develop a "Universal" Influenza Virus Vaccine? Immunogenetic Considerations Underlying B-Cell Biology in the Development of a Pan-Subtype Influenza A Vaccine Targeting the Hemagglutinin Stem.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018 Jul 2;10(7):a029413. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a029413. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018. PMID: 28663207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Broadly Reactive Influenza Antibodies Are Not Limited by Germinal Center Competition with High-Affinity Antibodies.mBio. 2020 Nov 3;11(6):e01859-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01859-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 33144374 Free PMC article.
-
B Cell Responses against Influenza Viruses: Short-Lived Humoral Immunity against a Life-Long Threat.Viruses. 2021 May 22;13(6):965. doi: 10.3390/v13060965. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34067435 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High preexisting serological antibody levels correlate with diversification of the influenza vaccine response.J Virol. 2015 Mar;89(6):3308-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02871-14. Epub 2015 Jan 14. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25589639 Free PMC article.
-
Low CD21 expression defines a population of recent germinal center graduates primed for plasma cell differentiation.Sci Immunol. 2017 Jan 27;2(7):eaai8153. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aai8153. Sci Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28783670 Free PMC article.
-
High Affinity Antibodies against Influenza Characterize the Plasmablast Response in SLE Patients After Vaccination.PLoS One. 2015 May 7;10(5):e0125618. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125618. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25951191 Free PMC article.
-
AID activity in B cells strongly correlates with polyclonal antibody affinity maturation in-vivo following pandemic 2009-H1N1 vaccination in humans.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Sep;8(9):e1002920. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002920. Epub 2012 Sep 13. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23028320 Free PMC article.
-
Antibodies in HIV-1 vaccine development and therapy.Science. 2013 Sep 13;341(6151):1199-204. doi: 10.1126/science.1241144. Science. 2013. PMID: 24031012 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barr IG, et al. Epidemiological, antigenic and genetic characteristics of seasonal influenza A(H1N1), A(H3N2) and B influenza viruses: Basis for the WHO recommendation on the composition of influenza vaccines for use in the 2009–2010 Northern Hemisphere season. Vaccine. 2010;28:1156–1167. - PubMed
-
- Carrat F, Flahault A. Influenza vaccine: The challenge of antigenic drift. Vaccine. 2007;25:6852–6862. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U19 AI090023/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI057158-06/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI076585/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI076585-04/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI057266/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1U19AI082724-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI062629-09/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI057158/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5U19AI062629-07/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 2U54AI057158-06/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI082724/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI090023-03/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R38 AI140299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 2U19AI057266-06/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI09023-01/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI062629/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI057266-09/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

