Transcriptome analysis and comparison reveal divergence between two invasive whitefly cryptic species
- PMID: 21939539
- PMCID: PMC3189941
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-458
Transcriptome analysis and comparison reveal divergence between two invasive whitefly cryptic species
Abstract
Background: Invasive species are valuable model systems for examining the evolutionary processes and molecular mechanisms associated with their specific characteristics by comparison with closely related species. Over the past 20 years, two species of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci species complex, Middle East-Asia Minor 1 (MEAM1) and Mediterranean (MED), have both spread from their origin Middle East/Mediterranean to many countries despite their apparent differences in many life history parameters. Previously, we have sequenced the transcriptome of MED. In this study, we sequenced the transcriptome of MEAM1 and took a comparative genomic approach to investigate the transcriptome evolution and the genetic factors underlying the differences between MEAM1 and MED.
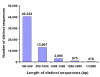
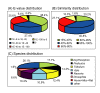
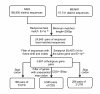
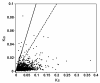
Results: Using Illumina sequencing technology, we generated 17 million sequencing reads for MEAM1. These reads were assembled into 57,741 unique sequences and 15,922 sequences were annotated with an E-value above 10-5. Compared with the MED transcriptome, we identified 3,585 pairs of high quality orthologous genes and inferred their sequence divergences. The average differences in coding, 5' untranslated and 3' untranslated region were 0.83%, 1.66% and 1.43%, respectively. The level of sequence divergence provides additional support to the proposition that MEAM1 and MED are two species. Based on the ratio of nonsynonymous and synonymous substitutions, we identified 24 sequences that have evolved in response to positive selection. Many of those genes are predicted to be involved in metabolism and insecticide resistance which might contribute to the divergence of the two whitefly species.
Conclusions: Our data present a comprehensive sequence comparison between the two invasive whitefly species. This study will provide a road map for future investigations on the molecular mechanisms underlying their biological differences.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysis of a native whitefly transcriptome and its sequence divergence with two invasive whitefly species.BMC Genomics. 2012 Oct 4;13:529. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-529. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23036081 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analyses reveal the adaptive features and biological differences of guts from two invasive whitefly species.BMC Genomics. 2014 May 15;15(1):370. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-370. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24885120 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the transcriptional differences between indigenous and invasive whiteflies reveals possible mechanisms of whitefly invasion.PLoS One. 2013 May 8;8(5):e62176. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062176. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23667457 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome sequencing of Asia II 1 species of whitefly reveals that genes involved in virus transmission and insecticide resistance have genetic variances between Asia II 1 and MEAM1 species.BMC Genomics. 2019 Jun 18;20(1):507. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5877-9. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31215403 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis and comparison reveal divergence between the Mediterranean and the greenhouse whiteflies.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 25;15(8):e0237744. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237744. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32841246 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
ASGARD: an open-access database of annotated transcriptomes for emerging model arthropod species.Database (Oxford). 2012 Nov 23;2012:bas048. doi: 10.1093/database/bas048. Print 2012. Database (Oxford). 2012. PMID: 23180770 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of whitefly transcriptional responses to Beauveria bassiana infection reveals new insights into insect-fungus interactions.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 5;8(7):e68185. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068185. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23861870 Free PMC article.
-
Omics approaches to unravel insecticide resistance mechanism in Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae).PeerJ. 2024 Sep 5;12:e17843. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17843. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39247549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolutionary Patterns of Sex-Biased Genes in Three Species of Haplodiploid Insects.Insects. 2020 May 26;11(6):326. doi: 10.3390/insects11060326. Insects. 2020. PMID: 32466547 Free PMC article.
-
High Variation in Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) and Insertions/Deletions (Indels) in the Highly Invasive Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) Middle East-Asia Minor 1 (MEAM1).Neotrop Entomol. 2013 Oct;42(5):521-6. doi: 10.1007/s13744-013-0152-2. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Neotrop Entomol. 2013. PMID: 23949985
References
-
- Stewart CNJ. Weedy and Invasive Plant Genomics. New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell; 2009.
-
- Smith CD, Zimin A, Holt C, Abouheif E, Benton R, Cash E, Croset V, Currie CR, Elhaik E, Elsik CG, Fave MJ, Fernandes V, Gadau J, Gibson JD, Graur D, Grubbs KJ, Hagen DE, Helmkampf M, Holley JA, Hu H, Viniegra AS, Johnson BR, Johnson RM, Khila A, Kim JW, Laird J, Mathis KA, Moeller JA, Munoz-Torres MC, Murphy MC, Nakamura R, Nigam S, Overson RP, Placek JE, Rajakumar R, Reese JT, Robertson HM, Smith CR, Suarez AV, Suen G, Suhr EL, Tao S, Torres CW, van Wilgenburg E, Viljakainen L, Walden KK, Wild AL, Yandell M, Yorke JA, Tsutsui ND. Draft genome of the globally widespread and invasive Argentine ant (Linepithema humile) Proc Nat Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:5673–5678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008617108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

