No evidence for statin-induced proteinuria in healthy volunteers as assessed by proteomic analysis
- PMID: 21918593
- PMCID: PMC3171927
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/456076
No evidence for statin-induced proteinuria in healthy volunteers as assessed by proteomic analysis
Abstract
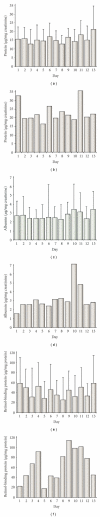
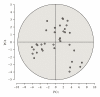
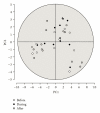
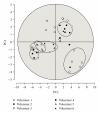
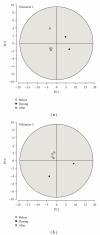
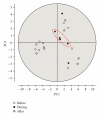
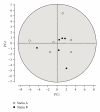
In clinical studies of statins (class of drugs lowering plasma cholesterol levels), transient low-molecular-weight proteinuria was observed. The causes of statin-induced proteinuria in the patient background of those studies (cardiovascular and kidney disease) are multifactorial and, therefore, a matter of debate. In light of this, it seemed interesting to investigate the effect of statins on the urinary protein concentration and proteome in healthy volunteers. Six healthy volunteers were randomly treated with rosuvastatin (40 mg/day) or pravastatin (80 mg/day) in a double-blinded cross-over study. Total urinary protein concentration and the concentration of albumin/retinol-binding protein were analysed, after which the urinary proteome was investigated. From the results described in this study, it was concluded that statins do not induce major changes in the urinary protein concentration/proteome. High variability in the baseline urinary proteome/proteins among volunteers, however, made it very difficult to find subtle (possibly isolated to individuals) effects of statins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
α1-Microglobulin/albumin ratio may improve interpretation of albuminuria in statin-treated patients.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013 Jul;51(7):1529-34. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2012-0798. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013. PMID: 23314557
-
Coadministration of dalcetrapib with pravastatin, rosuvastatin, or simvastatin: no clinically relevant drug-drug interactions.J Clin Pharmacol. 2010 Oct;50(10):1188-201. doi: 10.1177/0091270009358709. Epub 2010 May 20. J Clin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20489031 Clinical Trial.
-
An overview of statin-associated proteinuria.Drug Discov Today. 2006 May;11(9-10):458-64. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2006.03.017. Drug Discov Today. 2006. PMID: 16635810 Review.
-
Safety of rosuvastatin.Am J Cardiol. 2004 Oct 1;94(7):882-8. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2004.06.049. Am J Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 15464670 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of rosuvastatin in treatment of dyslipidemia.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2005 May 15;62(10):1033-47. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/62.10.1033. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2005. PMID: 15901588 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel therapeutic effect of statins on nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Feb;19(2):265-82. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12422. Epub 2015 Jan 16. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25594563 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tobert JA. Lovastatin and beyond: the history of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2003;2(7):517–526. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990;343(6257):425–430. - PubMed
-
- Ma P, Gil G, Sudhof TC, Bilheimer D, Goldstein J, Brown M. Mevinolin, an inhibitor of cholesterol synthesis, induces mRNA for low density lipoprotein receptor in livers of hamsters and rabbits. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1986;83(21):8370–8374. - PMC - PubMed
-
- McFarlane SI, Muniyappa R, Francisco R, Sowers JR. Clinical review 145: pleiotropic effects of statins: lipid reduction and beyond. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2002;87(4):1451–1458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

