Dual role of FoxA1 in androgen receptor binding to chromatin, androgen signalling and prostate cancer
- PMID: 21915096
- PMCID: PMC3209787
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.328
Dual role of FoxA1 in androgen receptor binding to chromatin, androgen signalling and prostate cancer
Abstract
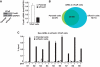
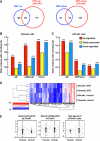
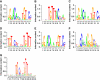
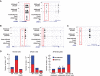
High androgen receptor (AR) level in primary tumour predicts increased prostate cancer-specific mortality. However, the mechanisms that regulate AR function in prostate cancer are poorly known. We report here a new paradigm for the forkhead protein FoxA1 action in androgen signalling. Besides pioneering the AR pathway, FoxA1 depletion elicited extensive redistribution of AR-binding sites (ARBs) on LNCaP-1F5 cell chromatin that was commensurate with changes in androgen-dependent gene expression signature. We identified three distinct classes of ARBs and androgen-responsive genes: (i) independent of FoxA1, (ii) pioneered by FoxA1 and (iii) masked by FoxA1 and functional upon FoxA1 depletion. FoxA1 depletion also reprogrammed AR binding in VCaP cells, and glucocorticoid receptor binding and glucocorticoid-dependent signalling in LNCaP-1F5 cells. Importantly, FoxA1 protein level in primary prostate tumour had significant association to disease outcome; high FoxA1 level was associated with poor prognosis, whereas low FoxA1 level, even in the presence of high AR expression, predicted good prognosis. The role of FoxA1 in androgen signalling and prostate cancer is distinctly different from that in oestrogen signalling and breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
FoxA1 specifies unique androgen and glucocorticoid receptor binding events in prostate cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2013 Mar 1;73(5):1570-80. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2350. Epub 2012 Dec 26. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23269278
-
Cooperativity and equilibrium with FOXA1 define the androgen receptor transcriptional program.Nat Commun. 2014 May 30;5:3972. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4972. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 24875621 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated levels of FOXA1 facilitate androgen receptor chromatin binding resulting in a CRPC-like phenotype.Oncogene. 2014 Dec 11;33(50):5666-74. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.508. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 24292680 Free PMC article.
-
FOXA1: a transcription factor with parallel functions in development and cancer.Biosci Rep. 2012 Apr 1;32(2):113-30. doi: 10.1042/BSR20110046. Biosci Rep. 2012. PMID: 22115363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pioneer of prostate cancer: past, present and the future of FOXA1.Protein Cell. 2021 Jan;12(1):29-38. doi: 10.1007/s13238-020-00786-8. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Protein Cell. 2021. PMID: 32946061 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin accessibility and pioneer factor FOXA1 restrict glucocorticoid receptor action in prostate cancer.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 25;52(2):625-642. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1126. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38015476 Free PMC article.
-
Human tRNAs with inosine 34 are essential to efficiently translate eukarya-specific low-complexity proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jul 9;49(12):7011-7034. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab461. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34125917 Free PMC article.
-
The genomic landscape of prostate cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 May 24;14(6):10822-51. doi: 10.3390/ijms140610822. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23708091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pioneer factors in hormone-dependent cancers.Nat Rev Cancer. 2012 May 4;12(6):381-5. doi: 10.1038/nrc3263. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22555282 Review.
-
Race and prostate cancer: genomic landscape.Nat Rev Urol. 2022 Sep;19(9):547-561. doi: 10.1038/s41585-022-00622-0. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Nat Rev Urol. 2022. PMID: 35945369 Review.
References
-
- Badve S, Turbin D, Thorat MA, Morimiya A, Nielsen TO, Perou CM, Dunn S, Huntsman DG, Nakshatri H (2007) FOXA1 expression in breast cancer – correlation with luminal subtype A and survival. Clin Cancer Res 13: 4415–4421 - PubMed
-
- Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, Wei G, Chepelev I, Zhao K (2007) High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 129: 823–837 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

