C2 domain-containing phosphoprotein CDP138 regulates GLUT4 insertion into the plasma membrane
- PMID: 21907143
- PMCID: PMC3172579
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.06.015
C2 domain-containing phosphoprotein CDP138 regulates GLUT4 insertion into the plasma membrane
Abstract
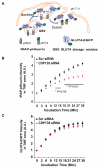
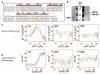
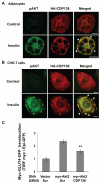
The protein kinase B(β) (Akt2) pathway is known to mediate insulin-stimulated glucose transport through increasing glucose transporter GLUT4 translocation from intracellular stores to the plasma membrane (PM). Combining quantitative phosphoproteomics with RNAi-based functional analyses, we show that a previously uncharacterized 138 kDa C2 domain-containing phosphoprotein (CDP138) is a substrate for Akt2, and is required for optimal insulin-stimulated glucose transport, GLUT4 translocation, and fusion of GLUT4 vesicles with the PM in live adipocytes. The purified C2 domain is capable of binding Ca(2+) and lipid membranes. CDP138 mutants lacking the Ca(2+)-binding sites in the C2 domain or Akt2 phosphorylation site S197 inhibit insulin-stimulated GLUT4 insertion into the PM, a rate-limiting step of GLUT4 translocation. Interestingly, CDP138 is dynamically associated with the PM and GLUT4-containing vesicles in response to insulin stimulation. Together, these results suggest that CDP138 is a key molecule linking the Akt2 pathway to the regulation of GLUT4 vesicle-PM fusion.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Crucial Role for the Small GTPase Rac1 Downstream of the Protein Kinase Akt2 in Insulin Signaling that Regulates Glucose Uptake in Mouse Adipocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 31;20(21):5443. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215443. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31683681 Free PMC article.
-
A novel pleckstrin homology domain-containing protein enhances insulin-stimulated Akt phosphorylation and GLUT4 translocation in adipocytes.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 3;285(36):27581-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.146886. Epub 2010 Jun 28. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20587420 Free PMC article.
-
Functional consequence of targeting protein kinase B/Akt to GLUT4 vesicles.J Cell Sci. 2002 Jul 15;115(Pt 14):2857-66. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115.14.2857. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 12082147
-
Myosin 5a is an insulin-stimulated Akt2 (protein kinase Bbeta) substrate modulating GLUT4 vesicle translocation.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jul;27(14):5172-83. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02298-06. Epub 2007 May 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17515613 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Function of PI(4,5)P2 in Insulin-Regulated Exocytic Trafficking of GLUT4 in Adipocytes.J Mol Biol. 2020 Jul 24;432(16):4341-4357. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.06.019. Epub 2020 Jun 25. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32593716
Cited by
-
Ethanolic Extract of Folium Sennae Mediates the Glucose Uptake of L6 Cells by GLUT4 and Ca2.Molecules. 2018 Nov 9;23(11):2934. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112934. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30424024 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of the human cyclin-dependent kinase family reveals a novel CDK5 complex involved in cell growth and migration.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014 Nov;13(11):2986-3000. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.036699. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 25096995 Free PMC article.
-
Dandelion Chloroform Extract Promotes Glucose Uptake via the AMPK/GLUT4 Pathway in L6 Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Nov 7;2018:1709587. doi: 10.1155/2018/1709587. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30524480 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying and Classifying Shared Selective Sweeps from Multilocus Data.Genetics. 2020 May;215(1):143-171. doi: 10.1534/genetics.120.303137. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Genetics. 2020. PMID: 32152048 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro and In Silico Analysis of PTP1B Inhibitors from Cleistocalyx operculatus Leaves and Their Effect on Glucose Uptake.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 24;16(17):2839. doi: 10.3390/nu16172839. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39275157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi DR, Caudwell FB, Andjelkovic M, Hemmings BA, Cohen P. Molecular basis for the substrate specificity of protein kinase B; comparison with MAPKAP kinase-1 and p70 S6 kinase. FEBS Lett. 1996;399:333–338. - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, James SR, Downes CP, Holmes AB, Gaffney PR, Reese CB, Cohen P. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Balpha. Curr Biol. 1997;7:261–269. - PubMed
-
- Bai J, Chapman ER. The C2 domains of synaptotagmin--partners in exocytosis. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004;29:143–151. - PubMed
-
- Bai L, Wang Y, Fan J, Chen Y, Ji W, Qu A, Xu P, James DE, Xu T. Dissecting multiple steps of GLUT4 trafficking and identifying the sites of insulin action. Cell Metab. 2007;5:47–57. - PubMed
-
- Bryant NJ, Govers R, James DE. Regulated transport of the glucose transporter GLUT4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:267–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

