Tumor cell-selective apoptosis induction through targeting of K(V)10.1 via bifunctional TRAIL antibody
- PMID: 21899742
- PMCID: PMC3179451
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-109
Tumor cell-selective apoptosis induction through targeting of K(V)10.1 via bifunctional TRAIL antibody
Abstract
Background: The search for strategies to target ion channels for therapeutic applications has become of increasing interest. Especially, the potassium channel K(V)10.1 (Ether-á-go-go) is attractive as target since this surface protein is virtually not detected in normal tissue outside the central nervous system, but is expressed in approximately 70% of tumors from different origins.
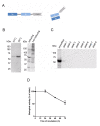
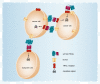
Methods: We designed a single-chain antibody against an extracellular region of K(V)10.1 (scFv62) and fused it to the human soluble TRAIL. The K(V)10.1-specific scFv62 antibody -TRAIL fusion protein was expressed in CHO-K1 cells, purified by chromatography and tested for biological activity.
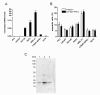
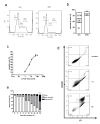
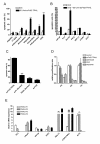
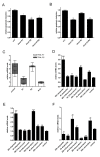
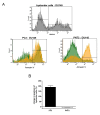
Results: Prostate cancer cells, either positive or negative for K(V)10.1 were treated with the purified construct. After sensitization with cytotoxic drugs, scFv62-TRAIL induced apoptosis only in K(V)10.1-positive cancer cells, but not in non-tumor cells, nor in tumor cells lacking K(V)10.1 expression. In co-cultures with K(V)10.1-positive cancer cells the fusion protein also induced apoptosis in bystander K(V)10.1-negative cancer cells, while normal prostate epithelial cells were not affected when present as bystander.
Conclusions: K(V)10.1 represents a novel therapeutic target for cancer. We could design a strategy that selectively kills tumor cells based on a K(V)10.1-specific antibody.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Guiding TRAIL to cancer cells through Kv10.1 potassium channel overcomes resistance to doxorubicin.Eur Biophys J. 2016 Oct;45(7):709-719. doi: 10.1007/s00249-016-1149-7. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Eur Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27350552 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling and enhanced activation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor-mediated apoptosis induction by an scFv:sTRAIL fusion protein with specificity for human EGFR.J Biol Chem. 2005 Mar 18;280(11):10025-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413673200. Epub 2005 Jan 11. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15644326
-
Engineered adenovirus fiber shaft fusion homotrimer of soluble TRAIL with enhanced stability and antitumor activity.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Jun 23;7(6):e2274. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.177. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27336718 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial dynamics of TRAIL death receptors in cancer cells.Drug Resist Updat. 2015 Mar;19:13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2015.02.001. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Drug Resist Updat. 2015. PMID: 25840763 Review.
-
Targeting miRNAs associated with surface expression of death receptors to modulate TRAIL resistance in breast cancer.Cancer Lett. 2016 Dec 28;383(2):154-160. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.09.021. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27693456 Review.
Cited by
-
Chlorpromazine binding to the PAS domains uncovers the effect of ligand modulation on EAG channel activity.J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 27;295(13):4114-4123. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.012377. Epub 2020 Feb 11. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32047112 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and characterization of novel recombinant anti-hERG1 scFv antibodies for cancer molecular imaging.Oncotarget. 2018 Oct 9;9(79):34972-34989. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26200. eCollection 2018 Oct 9. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30405887 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Ion Channels for Cancer Treatment: Current Progress and Future Challenges.Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2022;183:1-43. doi: 10.1007/112_2020_46. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 32865696 Review.
-
Targeting potassium channels in cancer.J Cell Biol. 2014 Jul 21;206(2):151-62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201404136. J Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25049269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guiding TRAIL to cancer cells through Kv10.1 potassium channel overcomes resistance to doxorubicin.Eur Biophys J. 2016 Oct;45(7):709-719. doi: 10.1007/s00249-016-1149-7. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Eur Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27350552 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

