IL-2 family cytokines: new insights into the complex roles of IL-2 as a broad regulator of T helper cell differentiation
- PMID: 21889323
- PMCID: PMC3405730
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2011.08.003
IL-2 family cytokines: new insights into the complex roles of IL-2 as a broad regulator of T helper cell differentiation
Abstract
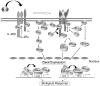
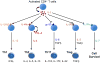
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is a pleiotropic cytokine that drives T-cell growth, augments NK cytolytic activity, induces the differentiation of regulatory T cells, and mediates activation-induced cell death. Along with IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21, IL-2 shares the common cytokine receptor γ chain, γ(c), which is mutated in humans with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. Herein, we primarily focus on the recently discovered complex roles of IL-2 in broadly modulating T cells for T helper cell differentiation. IL-2 does not specify the type of Th differentiation that occurs; instead, IL-2 modulates expression of receptors for other cytokines and transcription factors, thereby either promoting or inhibiting cytokine cascades that correlate with each Th differentiation state. In this fashion, IL-2 can prime and potentially maintain Th1 and Th2 differentiation as well as expand such populations of cells, whereas it inhibits Th17 differentiation but also can expand Th17 cells.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CD4⁺T cells: differentiation and functions.Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:925135. doi: 10.1155/2012/925135. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22474485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered Th1 cell differentiation programming by CIITA deficiency.J Immunol. 2004 Nov 1;173(9):5501-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.9.5501. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15494498
-
Interleukin-2 at the crossroads of effector responses, tolerance, and immunotherapy.Immunity. 2013 Jan 24;38(1):13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.01.004. Immunity. 2013. PMID: 23352221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine transcriptional events during helper T cell subset differentiation.J Exp Med. 1996 Aug 1;184(2):397-406. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.2.397. J Exp Med. 1996. PMID: 8760793 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of VIP on the balance between cytokines and master regulators of activated helper T cells.Immunol Cell Biol. 2012 Feb;90(2):178-86. doi: 10.1038/icb.2011.23. Epub 2011 Mar 29. Immunol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 21445087
Cited by
-
USP18 inhibits NF-κB and NFAT activation during Th17 differentiation by deubiquitinating the TAK1-TAB1 complex.J Exp Med. 2013 Jul 29;210(8):1575-90. doi: 10.1084/jem.20122327. Epub 2013 Jul 1. J Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 23825189 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of Schistosoma japonicum infection induced IFN-γ and IL-4 co-expressing plasticity Th cells.Immunology. 2016 Sep;149(1):25-34. doi: 10.1111/imm.12623. Immunology. 2016. PMID: 27242265 Free PMC article.
-
Humoral and T-cell-mediated responses to an insect-specific flavivirus-based Zika virus vaccine candidate.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Oct 10;20(10):e1012566. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012566. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39388457 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory effect of polysaccharides isolated from Lonicera japonica Thunb. in cyclophosphamide-treated BALB/c mice.Heliyon. 2022 Nov 25;8(11):e11876. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11876. eCollection 2022 Nov. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36458288 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of interleukin-2 level and genetic variants on coronary artery disease.Inflammation. 2013 Dec;36(6):1225-31. doi: 10.1007/s10753-013-9659-2. Inflammation. 2013. PMID: 23715819
References
-
- Morgan DA, Ruscetti FW, Gallo R. Selective in vitro growth of T lymphocytes from normal human bone marrows. Science. 1976;193:1007–1008. - PubMed
-
- Kim HP, Imbert J, Leonard WJ. Both integrated and differential regulation of components of the IL-2/IL-2 receptor system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006;17:349–366. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Rickert M, Garcia KC. Structure of the quaternary complex of interleukin-2 with its alpha, beta, and gammac receptors. Science. 2005;310:1159–1163. - PubMed
-
- Leonard WJ. Cytokines and immunodeficiency diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1:200–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

