Interactions of a Pop5/Rpp1 heterodimer with the catalytic domain of RNase MRP
- PMID: 21878546
- PMCID: PMC3185923
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2855511
Interactions of a Pop5/Rpp1 heterodimer with the catalytic domain of RNase MRP
Abstract
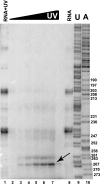
Ribonuclease (RNase) MRP is a multicomponent ribonucleoprotein complex closely related to RNase P. RNase MRP and eukaryotic RNase P share most of their protein components, as well as multiple features of their catalytic RNA moieties, but have distinct substrate specificities. While RNase P is practically universally found in all three domains of life, RNase MRP is essential in eukaryotes. The structural organizations of eukaryotic RNase P and RNase MRP are poorly understood. Here, we show that Pop5 and Rpp1, protein components found in both RNase P and RNase MRP, form a heterodimer that binds directly to the conserved area of the putative catalytic domain of RNase MRP RNA. The Pop5/Rpp1 binding site corresponds to the protein binding site in bacterial RNase P RNA. Structural and evolutionary roles of the Pop5/Rpp1 heterodimer in RNases P and MRP are discussed.
Figures

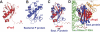

Similar articles
-
Footprinting analysis of interactions between the largest eukaryotic RNase P/MRP protein Pop1 and RNase P/MRP RNA components.RNA. 2015 Sep;21(9):1591-605. doi: 10.1261/rna.049007.114. Epub 2015 Jul 1. RNA. 2015. PMID: 26135751 Free PMC article.
-
Specific binding of a Pop6/Pop7 heterodimer to the P3 stem of the yeast RNase MRP and RNase P RNAs.RNA. 2007 Oct;13(10):1648-55. doi: 10.1261/rna.654407. Epub 2007 Aug 23. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17717080 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic ribonucleases P/MRP: the crystal structure of the P3 domain.EMBO J. 2010 Feb 17;29(4):761-9. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.396. Epub 2010 Jan 14. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20075859 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional similarities between MRP and RNase P.Mol Biol Rep. 1995-1996;22(2-3):81-5. doi: 10.1007/BF00988710. Mol Biol Rep. 1995. PMID: 8901492 Review.
-
The yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, RNase P/MRP ribonucleoprotein endoribonuclease family.Mol Biol Rep. 1995-1996;22(2-3):87-93. doi: 10.1007/BF00988711. Mol Biol Rep. 1995. PMID: 8901493 Review.
Cited by
-
Conserved regions of ribonucleoprotein ribonuclease MRP are involved in interactions with its substrate.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Aug;41(14):7084-91. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt432. Epub 2013 May 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23700311 Free PMC article.
-
GAMETOPHYTE DEFECTIVE 1, a putative subunit of RNases P/MRP, is essential for female gametogenesis and male competence in Arabidopsis.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e33595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033595. Epub 2012 Apr 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22509260 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro reconstitution and analysis of eukaryotic RNase P RNPs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 27;46(13):6857-6868. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky333. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29722866 Free PMC article.
-
Structural organizations of yeast RNase P and RNase MRP holoenzymes as revealed by UV-crosslinking studies of RNA-protein interactions.RNA. 2012 Apr;18(4):720-8. doi: 10.1261/rna.030874.111. Epub 2012 Feb 13. RNA. 2012. PMID: 22332141 Free PMC article.
-
Footprinting analysis of interactions between the largest eukaryotic RNase P/MRP protein Pop1 and RNase P/MRP RNA components.RNA. 2015 Sep;21(9):1591-605. doi: 10.1261/rna.049007.114. Epub 2015 Jul 1. RNA. 2015. PMID: 26135751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman S 2010. History of RNase P and overview of its catalytic activity. In Ribonuclease P, protein reviews 10 (ed. Liu F. and Altman S.), pp. 1–15 Springer, New York
-
- Brachmann CB, Davis A, Cost GJ, Caputo E, Li J, Hieter P, Boeke JD 1998. Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast 14: 115–132 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
