CD4+ T cells from elite suppressors are more susceptible to HIV-1 but produce fewer virions than cells from chronic progressors
- PMID: 21873218
- PMCID: PMC3174588
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1108866108
CD4+ T cells from elite suppressors are more susceptible to HIV-1 but produce fewer virions than cells from chronic progressors
Abstract
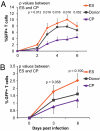
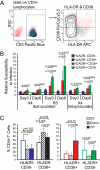
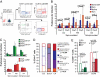
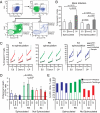
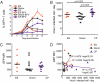
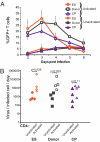
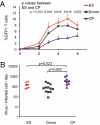
Elite suppressors/controllers (ES) are HIV-1-infected individuals who maintain stable CD4(+) T-cell counts and viral loads of <50 copies/mL without antiretroviral therapy. Research has predominantly focused on immune factors contributing to the control of viral replication in these patients. A more fundamental question, however, is whether there are differences in the nature of CD4(+) T-cell infection in ES compared with viremic patients. Here, we compare chronic progressor (CP), ES, and uninfected donors in terms of three aspects of CD4(+) T-cell infection: cellular susceptibility to infection, death of infected cells, and production of virus from infected cells. Using multiple methods of infection and both single-cycle and replication-competent virus, we show that unmanipulated CD4(+) T-cell populations from ES are actually more susceptible to HIV-1 infection than those populations from CP. Depletion of highly susceptible cells in CP may contribute to this difference. Using 7AAD and AnnexinV staining, we show that infected cells die more rapidly than uninfected cells, but the increased death of infected cells from CP and ES is proportional. Finally, using an assay for measuring virus production, we show that virus production by cells from CP is high compared with virus production by cells from ES or uninfected donors. This higher virus production is linked to cellular activation levels. These data identify fundamental differences in chronic infection of ES and CP that likely contribute to differential HIV-1 disease progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HLA-B*57 elite suppressor and chronic progressor HIV-1 isolates replicate vigorously and cause CD4+ T cell depletion in humanized BLT mice.J Virol. 2014 Mar;88(6):3340-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03380-13. Epub 2014 Jan 3. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24390323 Free PMC article.
-
Unstimulated primary CD4+ T cells from HIV-1-positive elite suppressors are fully susceptible to HIV-1 entry and productive infection.J Virol. 2011 Jan;85(2):979-86. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01721-10. Epub 2010 Nov 10. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21068257 Free PMC article.
-
Infrequent recovery of HIV from but robust exogenous infection of activated CD4(+) T cells in HIV elite controllers.Clin Infect Dis. 2010 Jul 15;51(2):233-8. doi: 10.1086/653677. Clin Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20550452 Free PMC article.
-
Effector mechanisms in HIV-1 infected elite controllers: highly active immune responses?Antiviral Res. 2010 Jan;85(1):295-302. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2009.08.007. Epub 2009 Sep 4. Antiviral Res. 2010. PMID: 19733595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elucidating the elite: mechanisms of control in HIV-1 infection.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009 Dec;30(12):631-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2009.09.005. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19837464 Review.
Cited by
-
Learning to Be Elite: Lessons From HIV-1 Controllers and Animal Models on Trained Innate Immunity and Virus Suppression.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 27;13:858383. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.858383. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35572502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV-1 elite controllers: an immunovirological review and clinical perspectives.J Virus Erad. 2019 Sep 18;5(3):163-166. doi: 10.1016/S2055-6640(20)30046-7. J Virus Erad. 2019. PMID: 31700663 Free PMC article.
-
Linking pig-tailed macaque major histocompatibility complex class I haplotypes and cytotoxic T lymphocyte escape mutations in simian immunodeficiency virus infection.J Virol. 2014 Dec;88(24):14310-25. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02428-14. Epub 2014 Oct 1. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25275134 Free PMC article.
-
Medroxyprogesterone acetate increases HIV-1 infection of unstimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro.AIDS. 2015 Jun 19;29(10):1137-46. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000681. AIDS. 2015. PMID: 26035316 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Mediated Immunity in Elite Controllers Naturally Controlling HIV Viral Load.Front Immunol. 2013 Apr 9;4:86. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00086. eCollection 2013. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23577012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Connell KA, Bailey JR, Blankson JN. Elucidating the elite: Mechanisms of control in HIV-1 infection. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009;30:631–637. - PubMed
-
- Migueles SA, Connors M. Long-term nonprogressive disease among untreated HIV-infected individuals: Clinical implications of understanding immune control of HIV. JAMA. 2010;304:194–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

