Stabilisation of p53 enhances reovirus-induced apoptosis and virus spread through p53-dependent NF-κB activation
- PMID: 21863032
- PMCID: PMC3185941
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2011.325
Stabilisation of p53 enhances reovirus-induced apoptosis and virus spread through p53-dependent NF-κB activation
Abstract
Background: Naturally oncolytic reovirus preferentially kills cancer cells, making it a promising cancer therapeutic. Mutations in tumour suppressor p53 are prevalent in cancers, yet the role of p53 in reovirus oncolysis is relatively unexplored.
Methods: Human cancer cell lines were exposed to Nutlin-3a, reovirus or a combination of the two and cells were processed for reovirus titration, western blot, real-time PCR and apoptosis assay using Annexin V and 7-AAD staining. Confocal microscopy was used to determine translocation of the NF-κB p65 subunit.
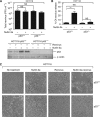
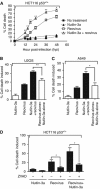
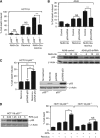
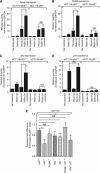
Results: We show that despite similar reovirus replication in p53(+/+) and p53(-/-) cells, stabilisation of p53 by Nutlin-3a significantly enhanced reovirus-induced apoptosis and hence virus release and dissemination while having no direct effect on virus replication. Enhanced apoptosis by Nutlin-3a was not observed in p53(-/-) or p53 knockdown cells; however, increased expression of Bax and p21 are required. Moreover, elevated NF-κB activation in reovirus-infected cells following Nutlin-3a treatment was necessary for enhanced reovirus-induced apoptosis, as synergistic cytotoxicity was overcome by specific NF-κB inhibitors.
Conclusion: Nutlin-3a treatment enhances reovirus-induced apoptosis and virus spread through p53-dependent NF-κB activation, and combination of reovirus and Nutlin-3a might represent an improved therapy against cancers harbouring wild-type p53.
Figures
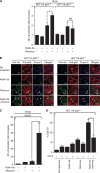
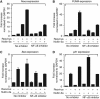
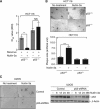
Similar articles
-
Activation of p53 by chemotherapeutic agents enhances reovirus oncolysis.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54006. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054006. Epub 2013 Jan 16. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23342061 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the p53 pathway by the MDM2 inhibitor nutlin-3a overcomes BCL2 overexpression in a preclinical model of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with t(14;18)(q32;q21).Leukemia. 2011 May;25(5):856-67. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.28. Epub 2011 Mar 11. Leukemia. 2011. PMID: 21394100 Free PMC article.
-
Nutlin-3a: A Potential Therapeutic Opportunity for TP53 Wild-Type Ovarian Carcinomas.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 6;10(8):e0135101. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135101. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26248031 Free PMC article.
-
Reovirus receptors, cell entry, and proapoptotic signaling.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;790:42-71. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-7651-1_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23884585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p53-independent roles of MDM2 in NF-κB signaling: implications for cancer therapy, wound healing, and autoimmune diseases.Neoplasia. 2012 Dec;14(12):1097-101. doi: 10.1593/neo.121534. Neoplasia. 2012. PMID: 23308042 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial p53 Contributes to Reovirus-Induced Neuronal Apoptosis and Central Nervous System Injury in a Mouse Model of Viral Encephalitis.J Virol. 2016 Aug 12;90(17):7684-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00583-16. Print 2016 Sep 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27307572 Free PMC article.
-
A Phase II Study of Pelareorep (REOLYSIN®) in Combination with Gemcitabine for Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2018 May 25;10(6):160. doi: 10.3390/cancers10060160. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29799479 Free PMC article.
-
The oncolytic virus, pelareorep, as a novel anticancer agent: a review.Invest New Drugs. 2015 Jun;33(3):761-74. doi: 10.1007/s10637-015-0216-8. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Invest New Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25693885 Review.
-
Curcumin inhibits Rift Valley fever virus replication in human cells.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 28;287(40):33198-214. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.356535. Epub 2012 Jul 30. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22847000 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of p53 by chemotherapeutic agents enhances reovirus oncolysis.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54006. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054006. Epub 2013 Jan 16. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23342061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alain T, Hirasawa K, Pon KJ, Nishikawa SG, Urbanski SJ, Auer Y, Luider J, Martin A, Johnston RN, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Lee PW, Kossakowska AE (2002) Reovirus therapy of lymphoid malignancies. Blood 100: 4146–4153 - PubMed
-
- Brown CJ, Lain S, Verma CS, Fersht AR, Lane DP (2009) Awakening guardian angels: drugging the p53 pathway. Nat Rev Cancer 9: 862–873 - PubMed
-
- Bunz F, Dutriaux A, Lengauer C, Waldman T, Zhou S, Brown JP, Sedivy JM, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1998) Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage. Science 282: 1497–1501 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

