Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 regulates bone mass, osteoblast gene expression, and responsiveness to parathyroid hormone
- PMID: 21852324
- PMCID: PMC3783352
- DOI: 10.1530/JOE-11-0144
Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 regulates bone mass, osteoblast gene expression, and responsiveness to parathyroid hormone
Abstract
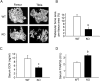
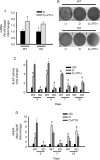
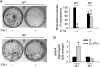
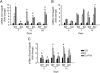
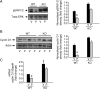
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) signaling via PTH 1 receptor (PTH1R) involves mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways. MAPK phosphatase 1 (MKP1) dephosphorylates and inactivates MAPKs in osteoblasts, the bone-forming cells. We previously showed that PTH1R activation in differentiated osteoblasts upregulates MKP1 and downregulates pERK1/2-MAPK and cyclin D1. In this study, we evaluated the skeletal phenotype of Mkp1 knockout (KO) mice and the effects of PTH in vivo and in vitro. Microcomputed tomography analysis of proximal tibiae and distal femora from 12-week-old Mkp1 KO female mice revealed osteopenic phenotype with significant reduction (8-46%) in bone parameters compared with wild-type (WT) controls. Histomorphometric analysis showed decreased trabecular bone area in KO females. Levels of serum osteocalcin (OCN) were lower and serum tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5b (TRAP5b) was higher in KO animals. Treatment of neonatal mice with hPTH (1-34) for 3 weeks showed attenuated anabolic responses in the distal femora of KO mice compared with WT mice. Primary osteoblasts derived from KO mice displayed delayed differentiation determined by alkaline phosphatase activity, and reduced expressions of Ocn and Runx2 genes associated with osteoblast maturation and function. Cells from KO females exhibited attenuated PTH response in mineralized nodule formation in vitro. Remarkably, this observation was correlated with decreased PTH response of matrix Gla protein expression. Expressions of pERK1/2 and cyclin D1 were inhibited dramatically by PTH in differentiated osteoblasts from WT mice but much less in osteoblasts from Mkp1 KO mice. In conclusion, MKP1 is important for bone homeostasis, osteoblast differentiation and skeletal responsiveness to PTH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
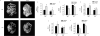
Similar articles
-
MKP1-dependent PTH modulation of bone matrix mineralization in female mice is osteoblast maturation stage specific and involves P-ERK and P-p38 MAPKs.J Endocrinol. 2013 Feb 25;216(3):315-29. doi: 10.1530/JOE-12-0372. Print 2013 Mar. J Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23197743 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles for mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) and ERK-MAPK in PTH1R signaling during osteoblast proliferation and differentiation.Cell Signal. 2010 Mar;22(3):457-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.10.017. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 19892016 Free PMC article.
-
Parathyroid hormone induces mitogen-activated kinase phosphatase 1 in murine osteoblasts primarily through cAMP-protein kinase A signaling.J Periodontol. 2006 Jan;77(1):21-30. doi: 10.1902/jop.2006.77.1.21. J Periodontol. 2006. PMID: 16579699
-
Anabolic effects of PTH in cyclooxygenase-2 knockout osteoblasts in vitro.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Aug 8;372(4):536-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.05.050. Epub 2008 May 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18501188 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of LRP6 in osteoblasts blunts the bone anabolic activity of PTH.J Bone Miner Res. 2013 Oct;28(10):2094-108. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1962. J Bone Miner Res. 2013. PMID: 23609180 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Parathyroid Hormone-Related Peptide and Its Analog, Abaloparatide, Attenuate Lethal Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 19;11(9):2273. doi: 10.3390/jcm11092273. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35566399 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical strain promotes osteoblast ECM formation and improves its osteoinductive potential.Biomed Eng Online. 2012 Oct 25;11:80. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-11-80. Biomed Eng Online. 2012. PMID: 23098360 Free PMC article.
-
Treadmill exercise influences the microRNA profiles in the bone tissues of mice.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Sep;22(3):1035. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10467. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34373721 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK phosphatase 1 inhibition of p38α within lung myofibroblasts is essential for spontaneous fibrosis resolution.J Clin Invest. 2024 Mar 21;134(10):e172826. doi: 10.1172/JCI172826. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38512415 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle and apoptosis regulatory protein (CARP)-1 is expressed in osteoblasts and regulated by PTH.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Jul 12;436(4):607-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.05.136. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23764399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beamer WG, Donahue LR, Rosen CJ. Genetics and bone. Using the mouse to understand man. Journal of Musculoskeletal & Neuronal Interactions. 2002;2:225–231. - PubMed
-
- Beamer WG, Shultz KL, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Horton LG, Delahunty KM, Coombs HF, III, Donahue LR, Canalis E, Rosen CJ. Genetic dissection of mouse distal chromosome 1 reveals three linked BMD QTLs with sex-dependent regulation of bone phenotypes. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 2007;22:1187–1196. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.070419. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

