HIV envelope gp120 activates LFA-1 on CD4 T-lymphocytes and increases cell susceptibility to LFA-1-targeting leukotoxin (LtxA)
- PMID: 21850260
- PMCID: PMC3151267
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023202
HIV envelope gp120 activates LFA-1 on CD4 T-lymphocytes and increases cell susceptibility to LFA-1-targeting leukotoxin (LtxA)
Abstract
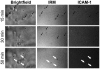
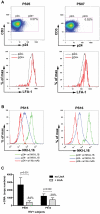
The cellular adhesion molecule LFA-1 and its ICAM-1 ligand play an important role in promoting HIV-1 infectivity and transmission. These molecules are present on the envelope of HIV-1 virions and are integral components of the HIV virological synapse. However, cellular activation is required to convert LFA-1 to the active conformation that has high affinity binding for ICAM-1. This study evaluates whether such activation can be induced by HIV itself. The data show that HIV-1 gp120 was sufficient to trigger LFA-1 activation in fully quiescent naïve CD4 T cells in a CD4-dependent manner, and these CD4 T cells became more susceptible to killing by LtxA, a bacterial leukotoxin that preferentially targets leukocytes expressing high levels of the active LFA-1. Moreover, virus p24-expressing CD4 T cells in the peripheral blood of HIV-infected subjects were found to have higher levels of surface LFA-1, and LtxA treatment led to significant reduction of the viral DNA burden. These results demonstrate for the first time the ability of HIV to directly induce LFA-1 activation on CD4 T cells. Although LFA-1 activation may enhance HIV infectivity and transmission, it also renders the cells more susceptible to an LFA-1-targeting bacterial toxin, which may be harnessed as a novel therapeutic strategy to deplete virus reservoir in HIV-infected individuals.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIV transfer between CD4 T cells does not require LFA-1 binding to ICAM-1 and is governed by the interaction of HIV envelope glycoprotein with CD4.Retrovirology. 2008 Mar 31;5:32. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-5-32. Retrovirology. 2008. PMID: 18377648 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging of HIV-1 envelope-induced virological synapse and signaling on synthetic lipid bilayers.J Vis Exp. 2012 Mar 8;(61):3757. doi: 10.3791/3757. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22433250 Free PMC article.
-
LFA-1 is a key determinant for preferential infection of memory CD4+ T cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1.J Virol. 2005 Nov;79(21):13714-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.21.13714-13724.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16227291 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of lymphomonocyte activation by HIV-1 glycoprotein gp120. Possible role in AIDS pathogenesis.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1996 Oct-Dec;10(4):83-91. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1996. PMID: 9604776 Review.
-
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin (LtxA; Leukothera®): Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Applications.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Aug 26;11(9):489. doi: 10.3390/toxins11090489. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31454891 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Leukotoxin (LtxA) Requires Death Receptor Fas, in Addition to LFA-1, To Trigger Cell Death in T Lymphocytes.Infect Immun. 2019 Jul 23;87(8):e00309-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00309-19. Print 2019 Aug. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 31109948 Free PMC article.
-
Leukotoxin kills rodent WBC by targeting leukocyte function associated antigen 1.Comp Med. 2013 Aug;63(4):331-7. Comp Med. 2013. PMID: 24209968 Free PMC article.
-
LFA-1-targeting Leukotoxin (LtxA; Leukothera®) causes lymphoma tumor regression in a humanized mouse model and requires caspase-8 and Fas to kill malignant lymphocytes.Leuk Res. 2015 Jun;39(6):649-56. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2015.03.010. Epub 2015 Mar 21. Leuk Res. 2015. PMID: 25850729 Free PMC article.
-
HIV Envelope gp120 Alters T Cell Receptor Mobilization in the Immunological Synapse of Uninfected CD4 T Cells and Augments T Cell Activation.J Virol. 2016 Nov 14;90(23):10513-10526. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01532-16. Print 2016 Dec 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27630246 Free PMC article.
-
A monoclonal antibody against lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 decreases HIV-1 replication by inducing the secretion of an antiviral soluble factor.Virol J. 2013 Apr 18;10:120. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-120. Virol J. 2013. PMID: 23594747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hioe CE, Bastiani L, Hildreth JE, Zolla-Pazner S. Role of cellular adhesion molecules in HIV type 1 infection and their impact on virus neutralization. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1998;14(Suppl 3):S247–254. - PubMed
-
- Capobianchi MR, Fais S, Castilletti C, Gentile M, Ameglio F, et al. A simple and reliable method to detect cell membrane proteins on infectious human immunodeficiency virus type 1 particles. J Infect Dis. 1994;169:886–889. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- D43 TWO1409/PHS HHS/United States
- R21 AI071815/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- D43 TW001409/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- AI080192/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX001411/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- DE16133/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI074286/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI044931/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-27742/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE016133/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027742/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI080606/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01-AI074286/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI044931/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI080192/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI044931/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI71815S/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI085958/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- IK6 BX004607/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- AI1007647/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI080606/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI71815/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AI085958/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

