Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in chronic lymphoid leukemia
- PMID: 21830940
- PMCID: PMC3387277
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1103849
Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in chronic lymphoid leukemia
Erratum in
-
Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells in Chronic Lymphoid Leukemia; Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells for Acute Lymphoid Leukemia; Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells for Sustained Remissions in Leukemia.N Engl J Med. 2016 Mar 10;374(10):998. doi: 10.1056/NEJMx160005. N Engl J Med. 2016. PMID: 26962747 No abstract available.
Abstract
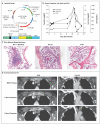
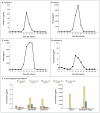
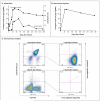
We designed a lentiviral vector expressing a chimeric antigen receptor with specificity for the B-cell antigen CD19, coupled with CD137 (a costimulatory receptor in T cells [4-1BB]) and CD3-zeta (a signal-transduction component of the T-cell antigen receptor) signaling domains. A low dose (approximately 1.5×10(5) cells per kilogram of body weight) of autologous chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells reinfused into a patient with refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) expanded to a level that was more than 1000 times as high as the initial engraftment level in vivo, with delayed development of the tumor lysis syndrome and with complete remission. Apart from the tumor lysis syndrome, the only other grade 3/4 toxic effect related to chimeric antigen receptor T cells was lymphopenia. Engineered cells persisted at high levels for 6 months in the blood and bone marrow and continued to express the chimeric antigen receptor. A specific immune response was detected in the bone marrow, accompanied by loss of normal B cells and leukemia cells that express CD19. Remission was ongoing 10 months after treatment. Hypogammaglobulinemia was an expected chronic toxic effect.
Figures
Comment in
-
Redirecting T cells.N Engl J Med. 2011 Aug 25;365(8):754-7. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1106965. Epub 2011 Aug 10. N Engl J Med. 2011. PMID: 21830939 No abstract available.
-
Chimeric antigen receptors: a costimulatory boost promotes immunological memory to B-cell malignancies.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011 Nov;11(11):1667-70. doi: 10.1586/era.11.159. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 22050014
-
Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in CLL.N Engl J Med. 2011 Nov 17;365(20):1937; author reply 1938. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1111004. N Engl J Med. 2011. PMID: 22087694 No abstract available.
-
Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in CLL.N Engl J Med. 2011 Nov 17;365(20):1937-8; author reply 1938. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1111004. N Engl J Med. 2011. PMID: 22087695 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for acute lymphoid leukemia.N Engl J Med. 2013 Apr 18;368(16):1509-1518. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1215134. Epub 2013 Mar 25. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 23527958 Free PMC article.
-
Chimeric antigen receptor T cells for sustained remissions in leukemia.N Engl J Med. 2014 Oct 16;371(16):1507-17. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1407222. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 25317870 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
T cells with chimeric antigen receptors have potent antitumor effects and can establish memory in patients with advanced leukemia.Sci Transl Med. 2011 Aug 10;3(95):95ra73. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002842. Sci Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21832238 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
CAR T Cell Therapy in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Potential for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2016 Jun;17(6):28. doi: 10.1007/s11864-016-0406-4. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27098534 Review.
-
[Treatment of lymphoblastic leukemia with CD19-specific modified chimeric antigen receptor T cells].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Dec;22(6):1753-6. doi: 10.7534/j.issn.1009-2137.2014.06.047. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25543510 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Regulatory considerations for clinical development of cancer vaccines.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(11):3409-14. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.982999. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25625933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Persistence and efficacy of second generation CAR T cell against the LeY antigen in acute myeloid leukemia.Mol Ther. 2013 Nov;21(11):2122-9. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.154. Epub 2013 Jul 8. Mol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23831595 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Receptor affinity and extracellular domain modifications affect tumor recognition by ROR1-specific chimeric antigen receptor T cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Jun 15;19(12):3153-64. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0330. Epub 2013 Apr 25. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23620405 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond CAR-T: The rise of CAR-NK cell therapy in asthma immunotherapy.J Transl Med. 2024 Aug 5;22(1):736. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05534-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39103889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A fully human chimeric antigen receptor with potent activity against cancer cells but reduced risk for off-tumor toxicity.Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 28;6(25):21533-46. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4071. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26101914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Irving BA, Weiss A. The cytoplasmic domain of the T cell receptor zeta chain is sufficient to couple to receptor-associated signal transduction pathways. Cell. 1991;64:891–901. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
