Prediction of ubiquitination sites by using the composition of k-spaced amino acid pairs
- PMID: 21829559
- PMCID: PMC3146527
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022930
Prediction of ubiquitination sites by using the composition of k-spaced amino acid pairs
Abstract
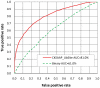
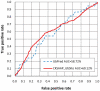
As one of the most important reversible protein post-translation modifications, ubiquitination has been reported to be involved in lots of biological processes and closely implicated with various diseases. To fully decipher the molecular mechanisms of ubiquitination-related biological processes, an initial but crucial step is the recognition of ubiquitylated substrates and the corresponding ubiquitination sites. Here, a new bioinformatics tool named CKSAAP_UbSite was developed to predict ubiquitination sites from protein sequences. With the assistance of Support Vector Machine (SVM), the highlight of CKSAAP_UbSite is to employ the composition of k-spaced amino acid pairs surrounding a query site (i.e. any lysine in a query sequence) as input. When trained and tested in the dataset of yeast ubiquitination sites (Radivojac et al, Proteins, 2010, 78: 365-380), a 100-fold cross-validation on a 1∶1 ratio of positive and negative samples revealed that the accuracy and MCC of CKSAAP_UbSite reached 73.40% and 0.4694, respectively. The proposed CKSAAP_UbSite has also been intensively benchmarked to exhibit better performance than some existing predictors, suggesting that it can be served as a useful tool to the community. Currently, CKSAAP_UbSite is freely accessible at http://protein.cau.edu.cn/cksaap_ubsite/. Moreover, we also found that the sequence patterns around ubiquitination sites are not conserved across different species. To ensure a reasonable prediction performance, the application of the current CKSAAP_UbSite should be limited to the proteome of yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
hCKSAAP_UbSite: improved prediction of human ubiquitination sites by exploiting amino acid pattern and properties.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Aug;1834(8):1461-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.04.006. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23603789
-
Prediction of mucin-type O-glycosylation sites in mammalian proteins using the composition of k-spaced amino acid pairs.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Feb 18;9:101. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-101. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18282281 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of protein phosphorylation sites by using the composition of k-spaced amino acid pairs.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046302. Epub 2012 Oct 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23110047 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of lysine crotonylation sites by incorporating the composition of k-spaced amino acid pairs into Chou's general PseAAC.J Mol Graph Model. 2017 Oct;77:200-204. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2017.08.020. Epub 2017 Aug 24. J Mol Graph Model. 2017. PMID: 28886434
-
Bioinformatics-aided Protein Sequence Analysis and Engineering.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2023;24(6):477-487. doi: 10.2174/1389203724666230509124300. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2023. PMID: 37287293 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of translesion DNA synthesis: Posttranslational modification of lysine residues in key proteins.DNA Repair (Amst). 2015 May;29:166-79. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.02.011. Epub 2015 Feb 18. DNA Repair (Amst). 2015. PMID: 25743599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A trans-specific polymorphism in ZC3HAV1 is maintained by long-standing balancing selection and may confer susceptibility to multiple sclerosis.Mol Biol Evol. 2012 Jun;29(6):1599-613. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mss002. Epub 2012 Jan 6. Mol Biol Evol. 2012. PMID: 22319148 Free PMC article.
-
DeepUbi: a deep learning framework for prediction of ubiquitination sites in proteins.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Feb 18;20(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2677-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30777029 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-based approaches for ubiquitination site prediction in human proteins.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Nov 28;24(1):449. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05581-w. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 38017391 Free PMC article.
-
RF-MaloSite and DL-Malosite: Methods based on random forest and deep learning to identify malonylation sites.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Mar 4;18:852-860. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.02.012. eCollection 2020. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 32322367 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

