A high resolution genome-wide scan of HNF4α recognition sites infers a regulatory gene network in colon cancer
- PMID: 21829439
- PMCID: PMC3145629
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021667
A high resolution genome-wide scan of HNF4α recognition sites infers a regulatory gene network in colon cancer
Abstract
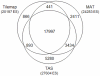
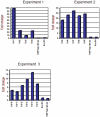
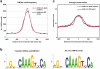
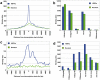
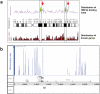
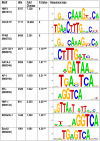
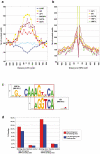
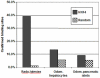
The hepatic nuclear factor HNF4α is a versatile transcription factor and controls expression of many genes in development, metabolism and disease. To delineate its regulatory gene network in colon cancer and to define novel gene targets a comprehensive genome-wide scan was carried out at a resolution of 35 bp with chromatin IP DNA obtained from the human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2 that is a particularly rich source of HNF4α. More than 90% of HNF4α binding sites were mapped as promoter distal sequences while enhancer elements could be defined to foster chromatin loops for interaction with other promoter-bound transcription factors. Sequence motif analysis by various genetic algorithms evidenced a unique enhanceosome that consisted of the nuclear proteins ERα, AP1, GATA and HNF1α as cooperating transcription factors. Overall >17,500 DNA binding sites were identified with a gene/binding site ratio that differed >6-fold between chromosomes and clustered in distinct chromosomal regions amongst >6600 genes targeted by HNF4α. Evidence is presented for nuclear receptor cross-talk of HNF4α and estrogen receptor α that is recapitulated at the sequence level. Remarkably, the Y-chromosome is devoid of HNF4α binding sites. The functional importance of enrichment sites was confirmed in genome-wide gene expression studies at varying HNF4α protein levels. Taken collectively, a genome-wide scan of HNF4α binding sites is reported to better understand basic mechanisms of transcriptional control of HNF4α targeted genes. Novel promoter distal binding sites are identified which form an enhanceosome thereby facilitating RNA processing events.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
The mouse fetoprotein transcription factor (FTF) gene promoter is regulated by three GATA elements with tandem E box and Nkx motifs, and FTF in turn activates the Hnf3beta, Hnf4alpha, and Hnf1alpha gene promoters.J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr 20;276(16):13136-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M010737200. Epub 2001 Jan 5. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11145965
-
Characterization of glucocorticoid receptor and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (HNF4alpha) binding to the hnf4alpha gene in the liver.Biochimie. 2009 Sep;91(9):1095-103. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2009.06.009. Epub 2009 Jun 21. Biochimie. 2009. PMID: 19540905
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α regulates the expression of the murine pyruvate carboxylase gene through the HNF4-specific binding motif in its proximal promoter.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1829(10):987-99. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.05.001. Epub 2013 May 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23665043
-
HNF4α--role in drug metabolism and potential drug target?Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010 Dec;10(6):698-705. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2010.08.010. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20833107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inverse regulation of claudin-2 and -7 expression by p53 and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α in colonic MCE301 cells.Tissue Barriers. 2021 Jan 2;9(1):1860409. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2020.1860409. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Tissue Barriers. 2021. PMID: 33356822 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Urate transport in health and disease.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Dec;35(4):101717. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2021.101717. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34690083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration analysis of microRNA and mRNA paired expression profiling identifies deregulated microRNA-transcription factor-gene regulatory networks in ovarian endometriosis.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2018 Jan 22;16(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12958-017-0319-5. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29357938 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Differences in Urate Handling.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 16;21(12):4269. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124269. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32560040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic occupancy of Runx2 with global expression profiling identifies a novel dimension to control of osteoblastogenesis.Genome Biol. 2014 Mar 21;15(3):R52. doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-3-r52. Genome Biol. 2014. PMID: 24655370 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA LINC00858 exerts a tumor-promoting role in colon cancer via HNF4α and WNK2 regulation.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020 Apr;43(2):297-310. doi: 10.1007/s13402-019-00490-8. Epub 2019 Dec 28. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020. PMID: 31884577
References
-
- Schrem H, Klempnauer J, Borlak J. Liver-enriched transcription factors in liver function and development. Part I: the hepatocyte nuclear factor network and liver-specific gene expression. Pharmacol Rev. 2002;54:129–158. - PubMed
-
- Rada-Iglesias A, Wallerman O, Koch C, Ameur A, Enroth S, et al. Binding sites for metabolic disease related transcription factors inferred at base pair resolution by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genomic microarrays. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14:3435–3447. - PubMed
-
- Delie F, Rubas W. A human colonic cell line sharing similarities with enterocytes as a model to examine oral absorption: advantages and limitations of the Caco-2 model. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 1997;14:221–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

