The mRNA-binding protein Zfp36 is upregulated by β-adrenergic stimulation and represses IL-6 production in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- PMID: 21818148
- PMCID: PMC4127993
- DOI: 10.1038/oby.2011.259
The mRNA-binding protein Zfp36 is upregulated by β-adrenergic stimulation and represses IL-6 production in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
Abstract
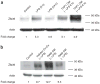
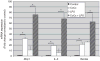
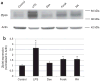
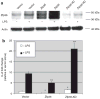
Obesity produces a chronic inflammatory state that contributes to the development of diabetes and atherosclerosis. In obese humans, fat depot adipocytes and macrophages produce inflammatory cytokines and other factors which exert unfavorable local and systemic immune responses. The expression of many cytokines is modulated at the post-transcriptional level by mRNA-binding proteins which recognize AU-rich elements (AREs) in the 3'-untranslated regions (3'-UTR) of these transcripts. One such protein, zinc finger protein 36 (Zfp36), is known to destabilize target mRNAs leading to decreased cytokine expression. Few regulators of Zfp36 expression in adipocytes have been described and mRNA targets of Zfp36 in adipocytes are largely unknown. We found that macrophage-derived inflammatory stimuli enhanced endogenous Zfp36 expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Furthermore, the β-adrenergic receptor agonist isoproterenol (Iso) and the glucocorticoid dexamethasone (Dex) each enhanced Zfp36 expression in adipocytes, the former most likely via a cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent pathway. By contrast, Zfp36 expression in murine macrophages (RAW 264.7) was not enhanced by exposure to Dex but was stimulated by retinoic acid (RA). Zfp36 inhibited basal and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated interleukin-6 (IL-6) expression in adipocytes. These data reveal important and cell type-specific modulators of Zfp36 expression in adipocytes and macrophages and identify Zfp36 as a potent repressor of adipocyte-derived IL-6. Furthermore, this work identifies new factors that stimulate adipocyte Zfp36 expression that are neither classically inflammatory nor mitogenic. Upregulating an mRNA-binding protein for therapeutic purposes may provide a novel mechanistic approach with which to treat diverse inflammatory disorders including common conditions associated with obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Insulin increases tristetraprolin and decreases VEGF gene expression in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008 Jun;16(6):1208-18. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.65. Epub 2008 Apr 3. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008. PMID: 18388887
-
Negative Feed-forward Control of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) by Tristetraprolin (ZFP36) Is Limited by the Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase, Dual-specificity Phosphatase 1 (DUSP1): IMPLICATIONS FOR REGULATION BY GLUCOCORTICOIDS.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 1;291(1):110-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.697599. Epub 2015 Nov 6. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26546680 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin (IL)-6 mRNA expression is stimulated by insulin, isoproterenol, tumour necrosis factor alpha, growth hormone, and IL-6 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Horm Metab Res. 2003 Mar;35(3):147-52. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-39075. Horm Metab Res. 2003. PMID: 12734774
-
Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Immune Responses and Inflammatory Diseases by RNA-Binding ZFP36 Family Proteins.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 1;12:711633. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.711633. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34276705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An IL-6 link between obesity and cancer.Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2013 Jan 1;5(2):461-78. doi: 10.2741/e628. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2013. PMID: 23277002 Review.
Cited by
-
Prostaglandin E2, but not cAMP nor β2-agonists, induce tristetraprolin (TTP) in human airway smooth muscle cells.Inflamm Res. 2019 May;68(5):369-377. doi: 10.1007/s00011-019-01224-0. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Inflamm Res. 2019. PMID: 30852628
-
A novel test for selection on cis-regulatory elements reveals positive and negative selection acting on mammalian transcriptional enhancers.Mol Biol Evol. 2013 Nov;30(11):2509-18. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst134. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Mol Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 23904330 Free PMC article.
-
Bronchial epithelial cell transcriptional responses to inhaled corticosteroids dictate severe asthmatic outcomes.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 Jun;151(6):1513-1524. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.01.028. Epub 2023 Feb 14. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36796454 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing of human non-hematopoietic bone marrow cells reveals a unique set of inter-species conserved biomarkers for native mesenchymal stromal cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Aug 30;14(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03437-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37649081 Free PMC article.
-
Deep sequencing of the transcriptome reveals inflammatory features of porcine visceral adipose tissue.Int J Biol Sci. 2013 Jun 9;9(6):550-6. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.6257. Print 2013. Int J Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23781149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferrante AW., Jr Obesity-induced inflammation: a metabolic dialogue in the language of inflammation. J Intern Med. 2007;262:408–414. - PubMed
-
- Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-α: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science. 1993;259:87–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

